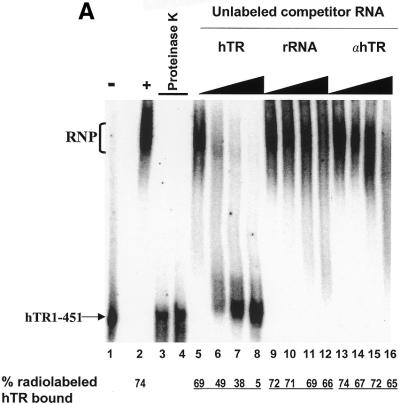
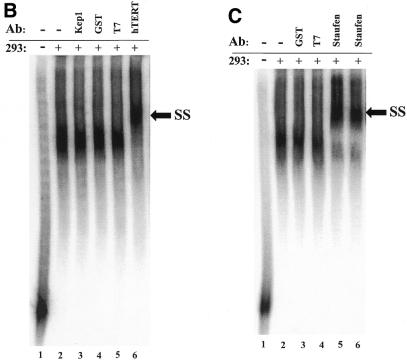
Figure 1.
Identification of a specific hTR–protein complex in vitro containing hTERT and human Staufen. (A) 32P-labeled hTR (0.25 pmol) was incubated in the absence (lane 1) or presence (lanes 2–16) of 3.4 µg partially purified telomerase extract from 293 cells that were (lanes 3 and 4) or were not (lanes 2 and 5–16) pretreated with proteinase K. The arrow points to the position of radiolabeled wild-type hTR, and the bracket indicates the RNP complex. In lanes 5–16, the binding reactions were performed with increasing concentrations (0.05, 0.4, 0.8 and 1.6 µM) of unlabeled specific hTR (hTR, lanes 5–8), non-specific E.coli 5S rRNA (rRNA, lanes 9–12) or antisense hTR (αhTR, lanes 13–16). The percentage (%) of radiolabeled complex-bound hTR is indicated at the bottom for each lane. (B and C) Identification of the catalytic subunit of human telomerase (hTERT) and the human Staufen protein in the specific hTR–protein complex using antibody supershift assays. Specific antibodies for hTERT and human Staufen, or control antibodies specific for the Drosophila RNA-binding protein Kep1, for the glutathione S-transferase (GST), and for the T7 epitope (T7) were added following the binding reactions as described in the Materials and Methods. The arrows indicate the respective supershifted (SS) complexes.