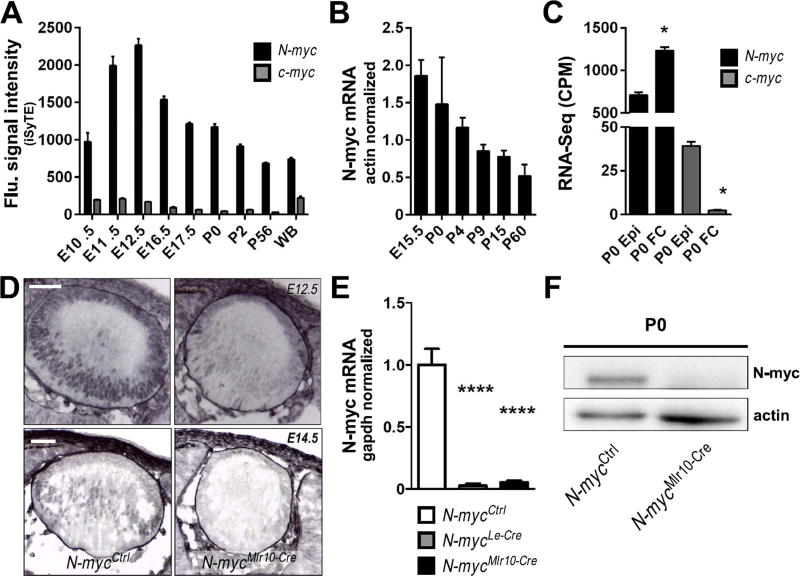
Fig. 1. N-myc expression is enriched in the developing mouse lens.
(A) iSyTE based expression of N-myc and c-myc mRNA in mouse lens at indicated embryonic and postnatal stages. (B) Realtime RT-PCR of N-myc mRNA in various stages of lens development (n = 3). Actb TaqMan probes were used to normalize. (C) N-myc and c-myc mRNA content in isolated lens epithelia or fiber cells at P0 (RNA-Seq analysis). (D) Immunohistochemistry for N-myc protein (purple) in cryosections of E12.5 and E14.5 lenses. No counterstaining was performed. (E) N-myc mRNA content (realtime RT-PCR) in P0 N-mycCtrl (n = 6), N-mycLe-Cre (n = 3) and N-mycMlr10-Cre (n = 3) lenses. GAPDH was used to normalize. (F) Representative western blot analysis of N-myc in P0 N-mycCtrl and N-mycMlr10-Cre lenses (actin was used as loading control) (n = 3). One-way ANOVA with Tukey's posttest performed in C. Error bars indicate S.E.M. in A and C and S.D. in B and E; *p < 0.05, **** p < 0. 0001. Scale bar: 50 µm. (WB: whole body reference; CPM: counts per million; Epi: lens epithelial cells; FC: lens fiber cells).