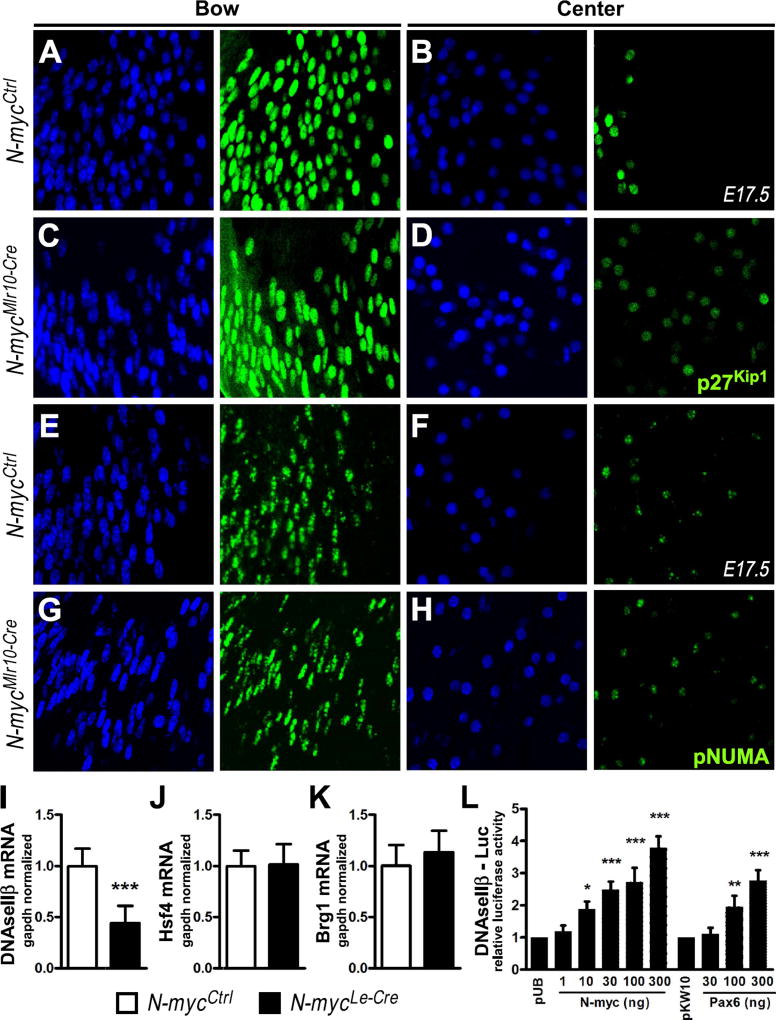
Fig. 7. Mechanisms of fiber cell denucleation in N-myc-deficient lenses.
(A-D) Representative pictures of p27Kip1 immunostaining (green) in the bow (A,C) vs. center (B,D) region of the lens in N-mycCtrl and N-mycMlr10-Cre E17.5 mice. (E-H) Representative pictures of phospho-NuMA (pNuMA) immunostaining (green) in the bow (E,G) vs. center (F,H) region of the lens in N-mycCtrl and N-mycMlr10-Cre E17.5 mice. DAPI used for nuclear counterstaining. (I-K) Realtime RT-PCR analysis of DNaseIIβ, Hsf4, and Brg1 mRNA content in P0 N-mycCtrl vs. N-mycLe-Cre lenses (n = 5). (L) Relative fold change in the luciferase activity of DNAseIIβ-luc reporter in α-TN4 cells transfected with N-myc or Pax6 as compared to empty-vector transfected cells (n = 3). t-test performed in I,J and K. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett's posttest performed in L. Error bars represent S.D. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Scale bar: 25 µm.