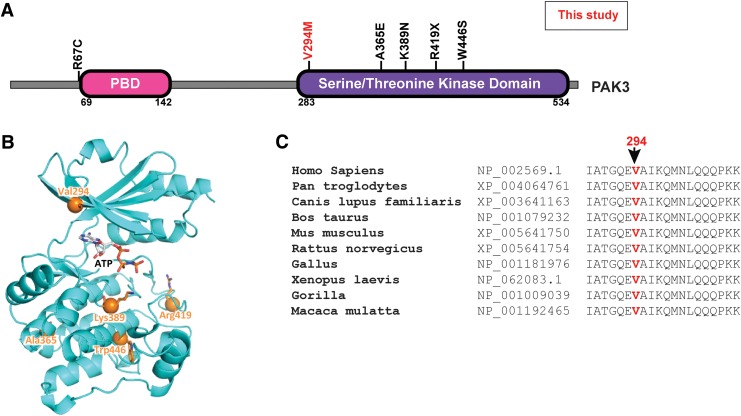
FIG. 2.
PAK3 mutation. (A) Graphical representation of PAK3 protein showing the conserved protein domains. Mutations in PAK3 that have been previously reported to cause XLID are shown in black and the mutation identified in this study is shown in red. (B) PAK3 mutations shown in the context of structure of PAK3 kinase domain. Homology model was generated using the closely related PAK1 structure as a template. An ATP molecule model is shown in sticks. V294 is on the “roof” of the ATP binding site. (C) Multiple sequence alignment of PAK3 homologs showing the residues and conservation of the mutated valine 294 site (red) in PAK3.