Figure 1.
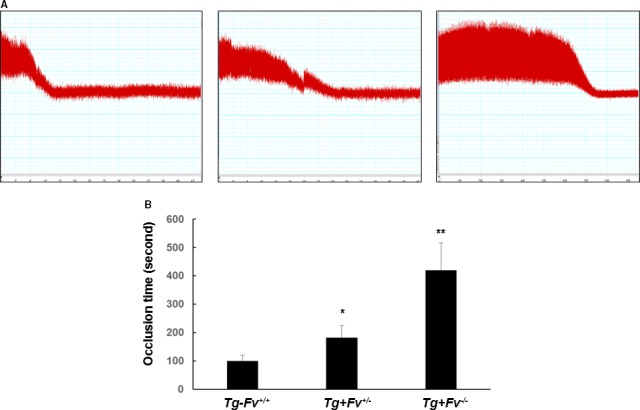
Carotid arterial occlusion after injury induced by ferric chloride (FeCl3). The carotid artery was injured by FeCl3 in the Tg‐Fv+/+, Tg+Fv+/−, and Tg+Fv−/− mice. The carotid artery blood flow tracings (A) and mean times to occlusion of the carotid arteries (B) are shown (n=9 per group). *P<0.05 vs the Tg‐Fv+/+ mice; **P<0.05 vs the Tg+Fv+/− mice.
