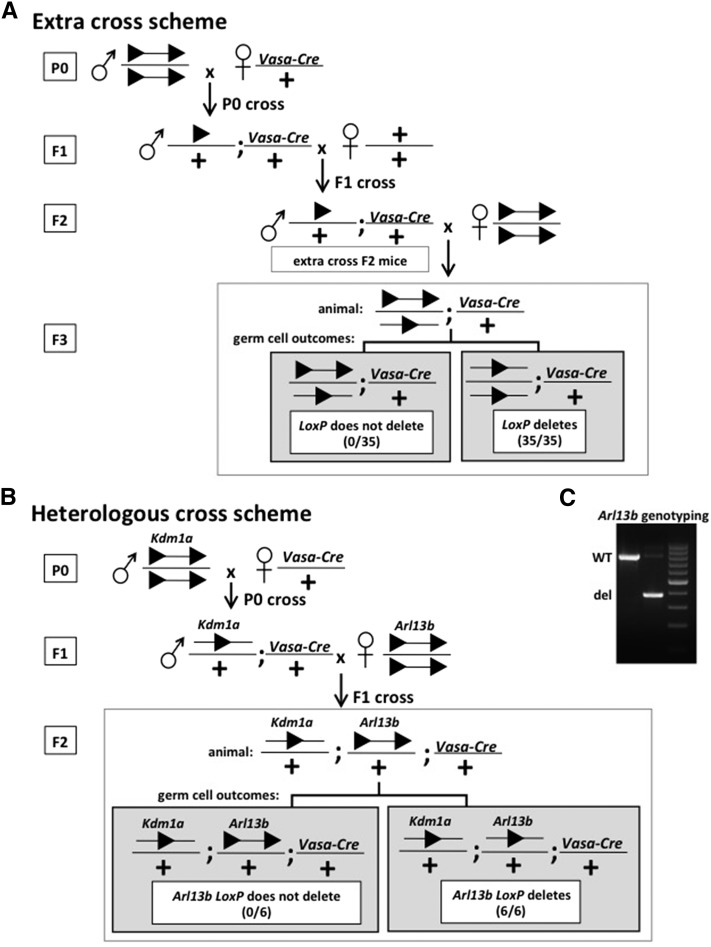
Figure 3.
Diagram of the extra cross (A) and heterologous cross (B) mating scheme. As in the original cross (Figure 1), floxed Kdm1a mice are initially crossed to Vasa-Cre to generate F1 heterozygotes. However, unlike in the original cross, the F1 heterozygotes are subsequently crossed to WT to generate extra cross F2 mice. These mice are genotypically identical to the original cross F1 mice (and their fathers), but differ in their parental history. Upon backcrossing to the floxed mice, the floxed allele in the germline of the extra cross F3 progeny now recombines with 100% efficiency. This was determined by genotyping the F4 progeny (see Materials and Methods and Figure S1 for details). (B) Alternatively, F1 heterozygotes are crossed to floxed Arl13b mice (heterologous cross). In the heterologous cross F2 mice, the Arl13b LoxP sequences recombine with 100% efficiency (see Materials and Methods and Figure S1 for details on how recombination was determined). (C) Sample genotyping showing the ability to distinguish Arl13b genotypes.