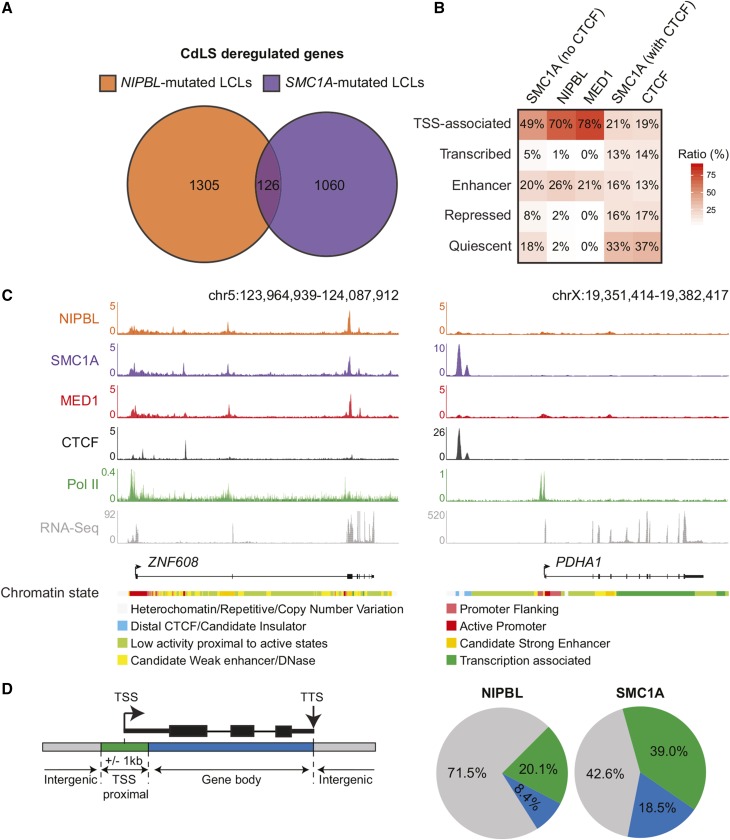
Figure 1.
NIPBL and cohesin occupy a fraction of CdLS-deregulated genes. (A) Genes affected by mutations in NIPBL and SMC1A are different. Venn diagram representation of differentially expressed genes in CdLS patient-derived LCLs with mutations in NIPBL and SMC1A. A total of 1431 and 1186 genes were identified in NIPBL- and SMC1A-mutated cell lines, respectively, while only 126 genes were shared (see Table S1 and Table S2). (B) Heatmap showing the percentage of overlap between regions occupied by SMC1A (no CTCF), NIPBL, MED1, SMC1A (with CTCF), and CTCF and the functional genome. A simplified version of the ChromHMM 18-state model in GM12878 cells (see Materials and Methods) was used to represent the functional genome. TSS-associated and enhancer regions are occupied by SMC1A (no CTCF) and NIPBL. The color scale indicates the ratio of overlap. (C) ChIP-Seq occupancy profiles of NIPBL, SMC1A, MED1, CTCF, and Pol II at the ZNF608 and PDHA1 loci, two CdLS-deregulated genes in GM12878 cells. RNA-Seq profiles show that both ZNF608 and PDHA1 genes are transcribed. The chromatin states are displayed below the gene tracks. Noncoding regulatory regions of the ZNF608 locus are occupied by SMC1A and NIPBL while they are not for PDHA1. The scales of ChIP-Seq and RNA-Seq profiles are displayed in reads per million. (D) NIPBL and SMC1A occupancy of deregulated genes in CdLS. Percentage of deregulated genes in NIPBL-mutated or SMC1A-mutated cells occupied by NIPBL or SMC1A respectively. Regions associated to genes were defined as: TSS proximal (a ±1 kb region surrounding the TSS), gene body (from +1 kb to the TTS), and intergenic (not TSS proximal nor gene body). Overall, 71.5% of genes deregulated in NIPBL-mutated cells are not occupied by NIPBL, while 42.6% of genes deregulated in SMC1A-mutated cells are not occupied by SMC1A. CdLS, Cornelia de Lange syndrome; ChIP-Seq, chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing; chr, chromosome; LCLs, lymphoblastoid cell lines; Pol II, RNA polymerase II; RNA-Seq, RNA sequencing; TSS, transcription start site; TTS, transcription termination site.