Figure 4.
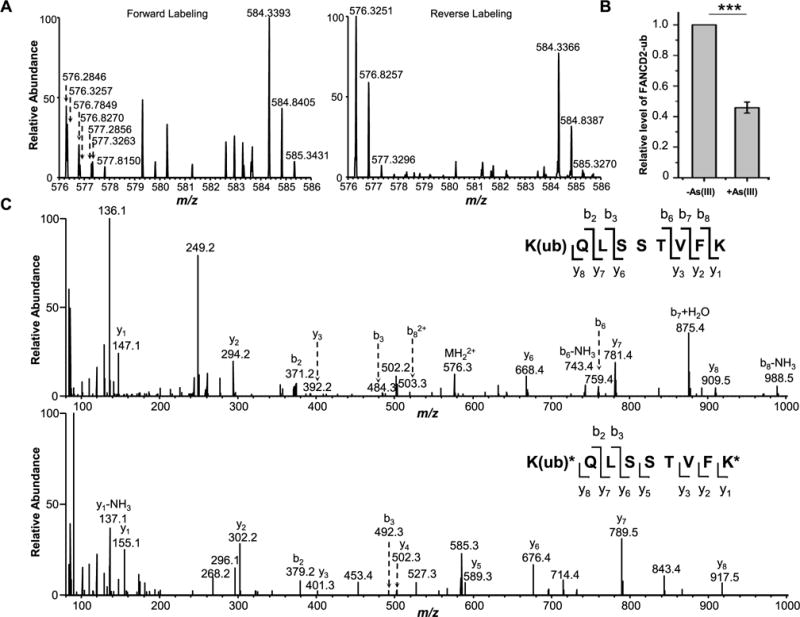
Diminished monoubiquitination of FANCD2 after arsenite treatment in GM00637 cells as revealed by LC-MS/MS data. (A) MS results for FANCD2 K561 ubiquitination from the forward and reverse SILAC labeling samples. In the forward sample, cells cultured in light SILAC medium were treated with 5 μM NaAsO2 for 24 h and mixed with an equal amount of lysate from untreated cells cultured in heavy SILAC medium. In the reverse sample, lysate of cells cultured in heavy medium and treated with 5 μM NaAsO2 was mixed with an equal amount of lysate of untreated cells cultured in light medium. The spectrum shows the [M + 2H]2+ ions for FANCD2 K(ub)QLSSTVFK (light, m/z 576.3217) and K(ub)*QLSSTVFK* (heavy, m/z 584.3246) peptides. (B) Relative levels of ubiquitination of K561 in FANCD2 with or without arsenite treatment. The data represent the mean and standard deviation of results obtained from three independent experiments. The level of FANCD2 ubiquitination in the control group was normalized into 1.0. ***P < 0.001, and the P values were calculated using a two-tailed, unpaired Student’s t test. (C) MS/MS results for K(ub)QLSSTVFK (light) and K(ub)*QLSSTVFK* (heavy) peptides.
