Figure 2.
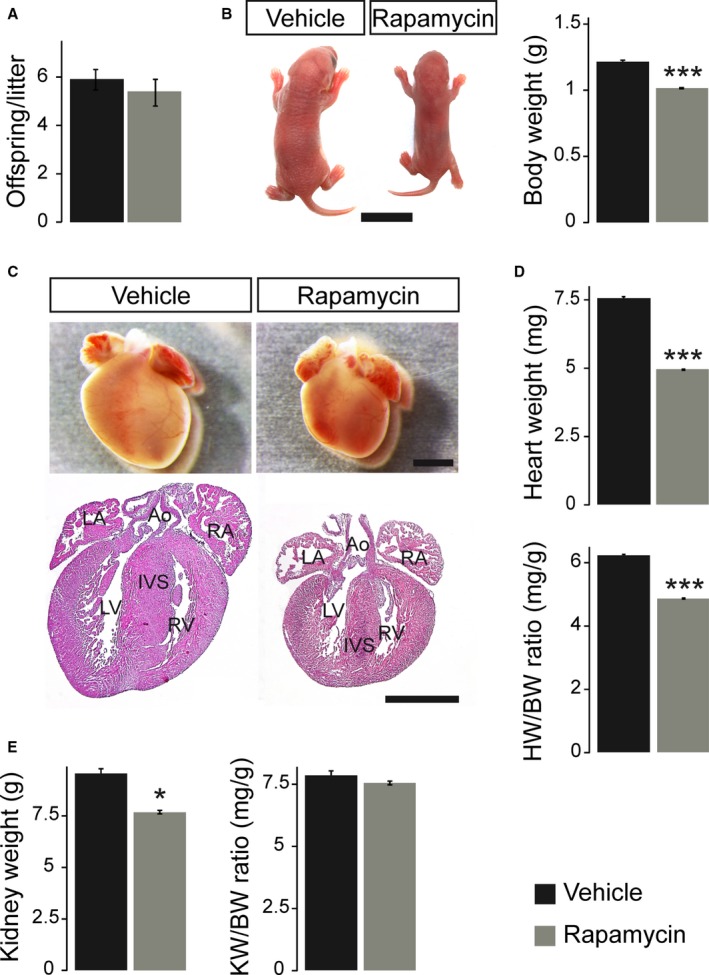
Prenatal rapamycin treatment causes IUGR and reduces heart size at birth. A, Average litter size of vehicle‐ and rapamycin‐treated dams did not differ on postnatal day 1 (n=9 litters per treatment group). B, Newborn offspring after prenatal rapamycin treatment were smaller compared to vehicle‐treated controls (scale bar=1 cm), resulting in significantly reduced body weight (BW). C, Neonatal mice after prenatal rapamycin treatment had smaller hearts compared to their vehicle controls but did not exhibit major structural or morphological cardiac defects (hematoxylin and eosin staining in lower panel, scale bars=1 mm; Ao indicates aorta; IVS, interventricular septum; IUGR, intrauterine growth restriction; LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricle; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle). D, Rapamycin‐treated neonates demonstrated significantly lower heart weight (HW) and HW/BW ratio compared to vehicle‐treated animals. E, Even though kidney weight (KW) of rapamycin‐treated neonates was significantly reduced compared to vehicle‐treated animals, the KW/BW ratio was not altered. B, D, and E, Vehicle n=9, rapamycin n=10. (***P<0.001, *P<0.05).
