Figure 5.
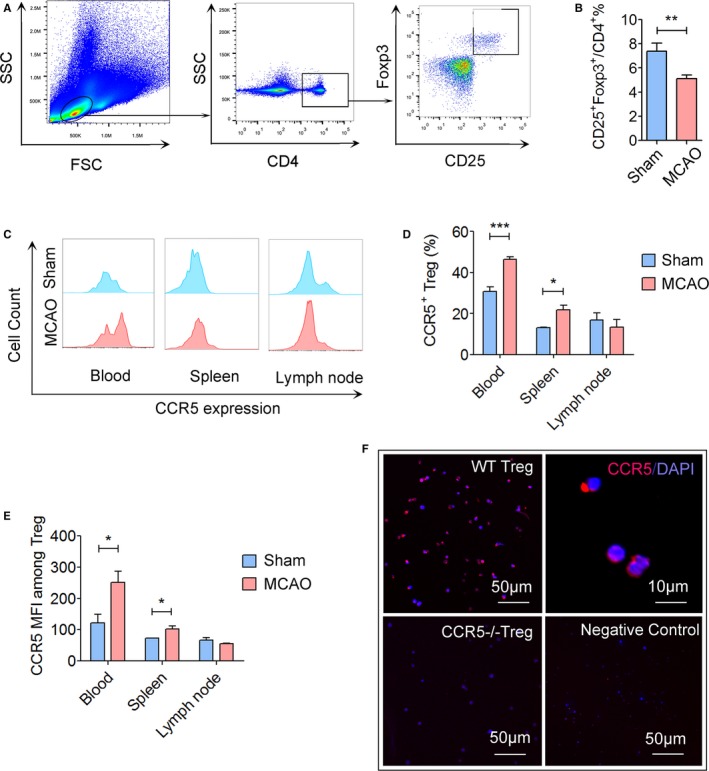
Expression of CCR5 is upregulated on peripheral Tregs after cerebral ischemic stroke. Cerebral ischemia was induced in mice by transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO) for 60 minutes. Blood, spleen, and lymph nodes were collected for flow cytometry analysis at 1 day after reperfusion. A, Gating strategy for CD4+ CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs in the blood. B, Quantification of CD4+ CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs among CD4+ lymphocytes in the blood at 1 day after MCAO or sham operation. Cerebral ischemia reduced the percentage of CD4+ CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs. C, Representative flow cytometry plots of CCR5 expression on Tregs in the blood, spleen, and lymph nodes at 1 day after sham or tMCAO. D, Quantification of CCR5+ cells among Tregs. E, Quantification of CCR5 mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) on Tregs at 1 day after sham or tMCAO, n=5 to 6/group. F, Immunostaining of CCR5 on Tregs collected from C57/BL6 wild type (WT) mice or CCR5−/− mice. Representative images are from 2 repeats of independent experiments. *P≤0.05, **P≤0.01, ***P≤0.001. CCR5 indicates C‐C chemokine receptor type 5; Treg, regulatory T cell. FSC, forward scatter; SSC, side scatter.
