Figure 6.
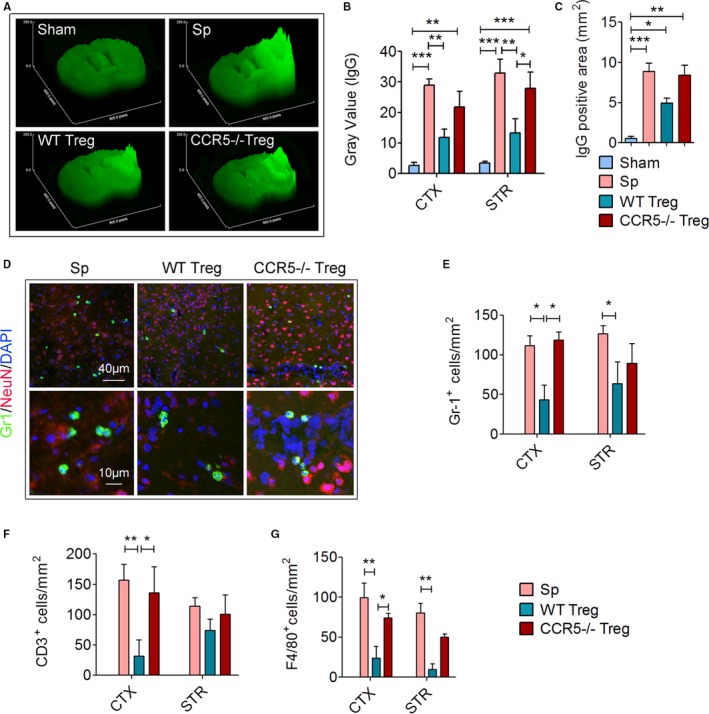
CCR5 expression by transferred Tregs plays an important role in their protective effect against blood‐brain barrier (BBB) disruption early after stroke. Splenocytes (Sp), wild type (WT) Tregs or CCR5−/− Tregs (2×106) were adoptively transferred into stroke mice 2 hours after 60 minutes of transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (tMCAO). Brain sections were collected 1 day after tMCAO. A through C, Brain sections were stained for endogenous plasma IgG to detect BBB leakage (n=6/group). A, Representative surface plot images of endogenous IgG from sham or tMCAO mice treated with WT or CCR5−/− Treg. B, Quantification of gray value of brain sections in A. C, Quantification of positive IgG‐stained area of brain sections in A. D through G, Brain sections were stained with Gr‐1, a neutrophil marker, CD3, a T‐cell marker, and F4/80, a macrophage marker (n=6/group). D, Representative images showing the infiltration of Gr‐1+ neutrophils into the ischemic brain. E, Quantification of the number of Gr‐1+ neutrophils in the ischemic brain (n=5/group). F, Quantification of the number of CD3+ T cells in the ischemic brain. G, Quantification of the number of F4/80+ macrophages in the ischemic brain. *P≤0.05, **P≤0.01, ***P≤0.001. CCR5 indicates C‐C chemokine receptor type 5; CTX, cortex; IgG, immunoglobulin G; STR, striatum; Treg, regulatory T cell.
