Figure 1.
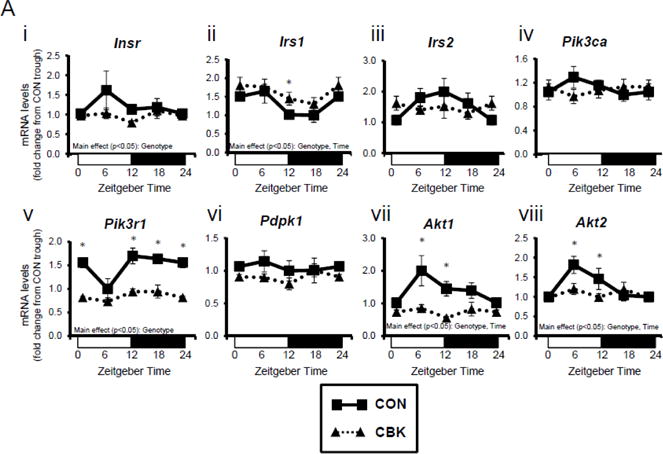
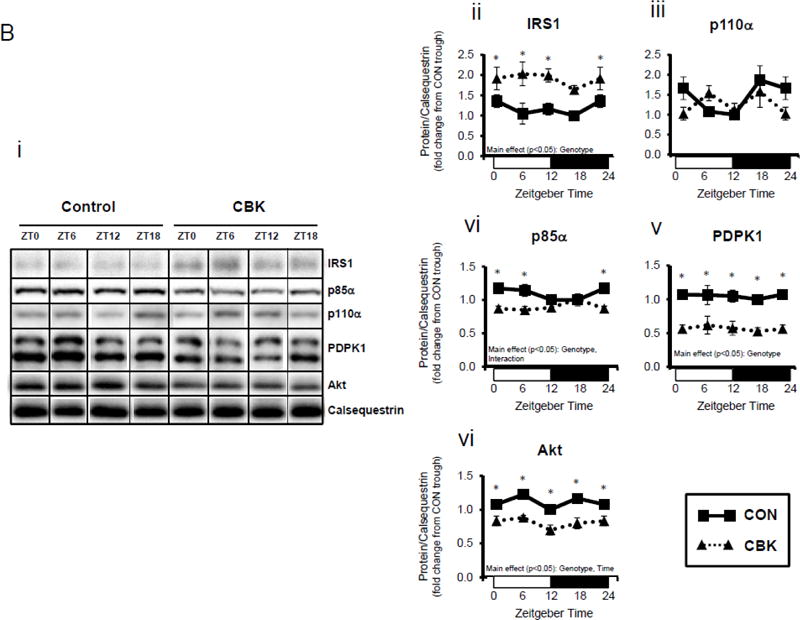
Genetic ablation of the cardiomyocyte circadian clock influences diurnal variations in mRNA (A) and protein (B) levels of key insulin-signaling components in the heart. CBK and littermate control (CON) mouse hearts were collected at distinct times of day, followed by RT-PCR (A; 4–7 independent observations) and Western blot (B; n=4–7 independent observations) analysis. Data are represented as fold change from the trough of CON hearts. Data for ZT0 is duplicated as ZT24 for visualization purposes only. All data are shown as mean ± SEM. *, p<0.05 for CBK versus CON hearts within a ZT.
