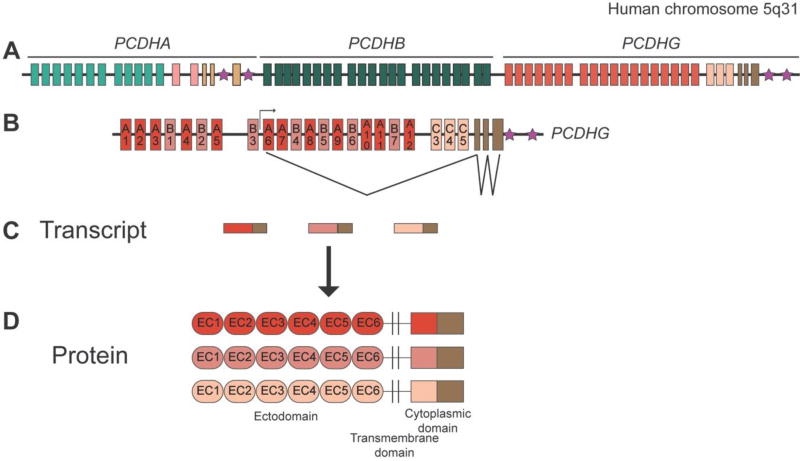
Figure 2. The protocadherin gene clusters.
A: Schematic of the human PCDHA, PCDHB, and PCDHG gene clusters on chromosome 5q31. A very similar structure is observed for the mouse clusters at chromosome 18. B: The exon structure of the PCDHG cluster is expanded below, with an example of the transcription initiation and splicing pattern (for A6, in this instance). C: Schematic of the PCDHG spliced transcripts generated by the cluster; each mature transcript consists of one large variable exon and the three small constant exons. D: Protein structure of the γ-Pcdhs (α-Pcdhs are identical in structure; β-Pcdhs lack any constant domain). Six extracellular cadherin (EC) repeats, a transmembrane domain, and a variable cytoplasmic domain are encoded by each variable exon; the constant exons encode a 125 amino acid C-terminal domain. Stars indicate the sites of “cluster control regions”, enhancers required for normal expression patterns of the Pcdh clusters.