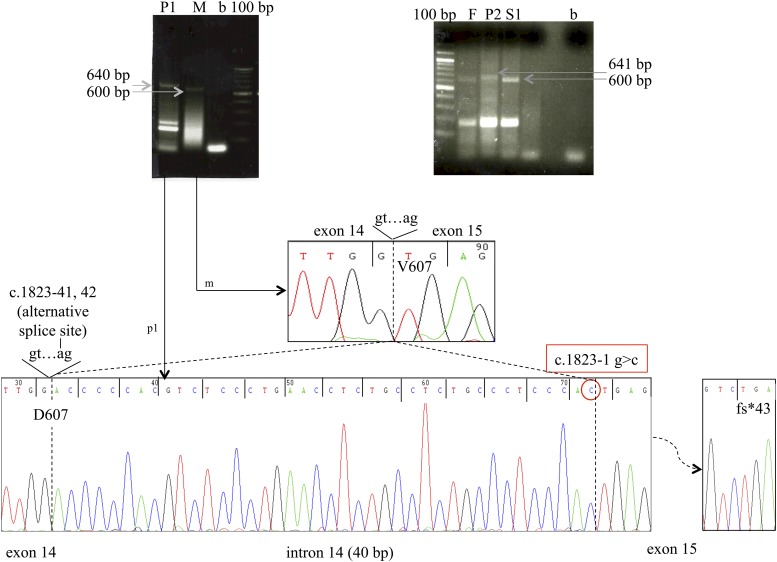
Figure 2.
Complementary DNA amplification and sequencing from homozygous and heterozygous family members, demonstrating aberrant splicing of DUOX1. The electropherogram of the complementary DNAs and transcript sizes of the different DUOX1 variants detected in the family members are shown. Exons are numbered with the first translated exon as exon 1. P1, P2: children with CH and homozygous DUOX1 c.1823-1G>C mutation. M, mother; F, father; S1, sister; all unaffected and heterozygous for the DUOX1 c.1823-1G>C mutation.