Figure 10.
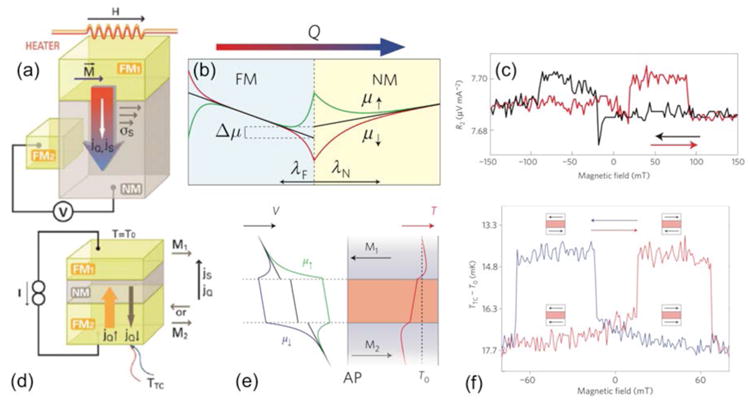
Spin-dependent Seebeck (panels a-c) and Peltier (panels d-f) effects for conduction electrons: (a) non-local geometry used for observation of spin-dependent Seebeck effect [Boona et al., 2014]; (b) expected spatial dependence of spin-dependent chemical potentials compared to spin diffusion lengths in ferromagnets (FM) and non-magnets (NM) and (c) thermally-driven spin accumulation signal [Slachter et al., 2010]; (d) Structure used for Onsager reciprocal spin-dependent Peltier effect [Boona et al., 2014]; (e) expected spin-dependent chemical potentials for antiparallel alignment of FM elements, clarifying the short length scale probed and (f) current-driven spin-dependent temperature difference [Flipse et al., 2012].
