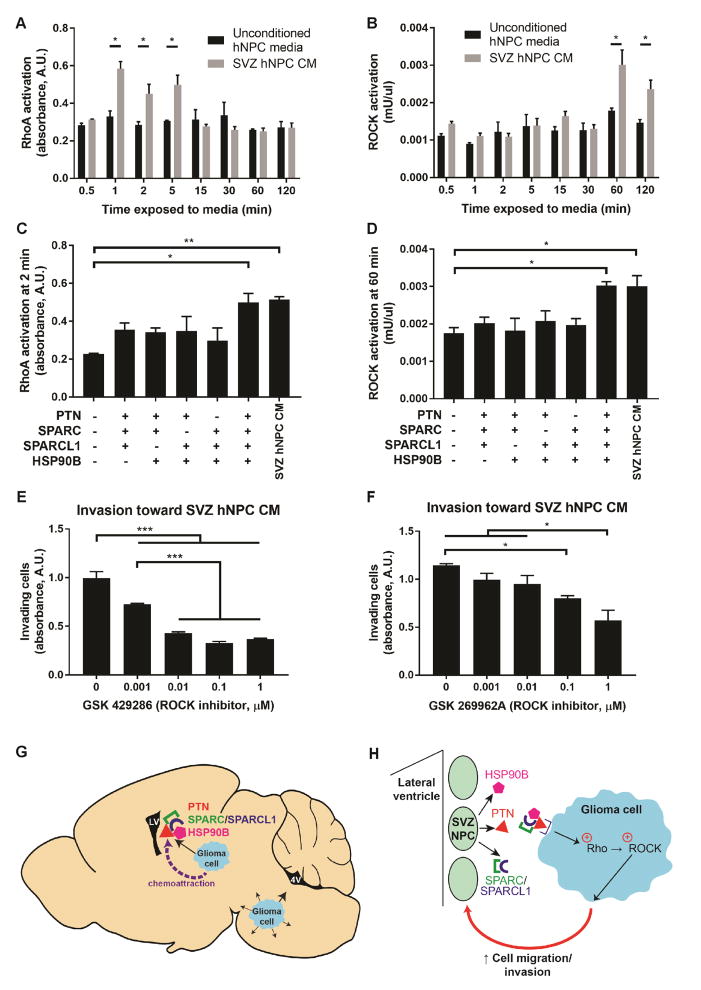
Figure 7. NPC-secreted factors activate the Rho/ROCK pathway.
See also Figure S7.
(A–B) Exposure of DIPG cells to SVZ hNPC CM activated RhoA after 1–5 minutes (A) and ROCK after 60–120 minutes (B), compared to unconditioned hNPC media.
(C–D) Exposure to PTN and the three binding partners in unconditioned hNPC media activated RhoA (C) and ROCK (D) similarly to SVZ hNPC CM.
(E–F) Treatment with ROCK inhibitors GSK 429286 or GSK 269962A decreased DIPG invasion toward SVZ hNPC CM in a dose-dependent manner.
All experiments performed with n = 3 replicates/wells in SU-DIPG-XIII FL cells and analyzed by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-tests for comparison between unconditioned and conditioned hNPC media (A–B) or by one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc adjustment for multiple comparisons (C–F). Data shown as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
(G) Schematic illustrating the model of glioma cells originating in the pons invading generally in the ventral pons, and being drawn at short to medium range into the SVZ upon exposure to PTN and the three binding partners secreted by SVZ NPCs.
(H) Schematic illustrating the model of glioma chemoattraction toward NPC-secreted PTN and the three binding partners, subsequent activation of the Rho/ROCK pathway in glioma cells, and promotion of glioma cell migration and invasion.