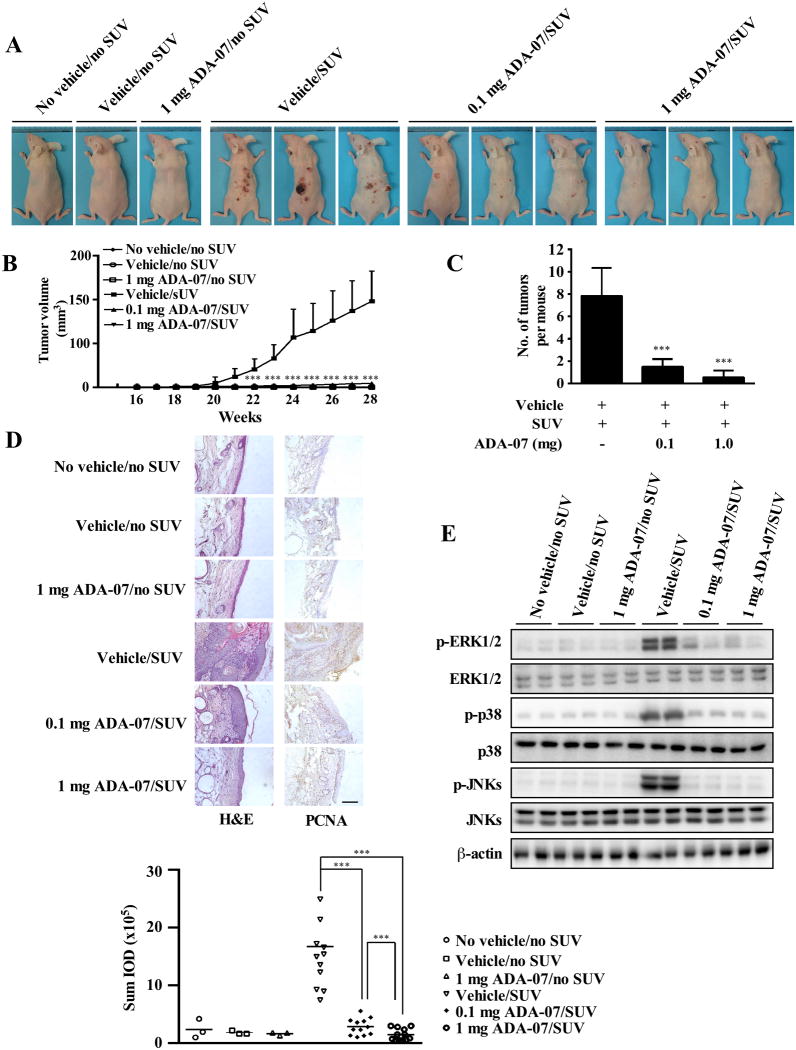
Figure 5. ADA-07 suppresses SUV-induced skin carcinogenesis in an SKH-1 hairless mouse late-stage prevention model.
SKH-1 hairless mice were treated as described in Materials and Methods. Mice were exposed to SUV for 15 weeks and then treatment with vehicle with or without ADA-07 was applied topically to the dorsal area for an additional 13 weeks. Tumor incidence and multiplicity were recorded weekly until the end of the experiment at week 28. A, external appearance of tumors. B, ADA-07 suppresses SUV-induced tumor volume. Tumor volume was calculated according to the following formula: tumor volume (mm3) = length × width × height × 0.52. C, ADA-07 decreases the average number of SUV-induced tumors at week 28. For B and C, data are represented as mean values ± S.D. and differences were determined by one-way ANOVA. The asterisk (*) indicates a significant decrease compared to the group exposed to SUV only or the group treated with vehicle followed by SUV (***, p < 0.001). D, ADA-07 inhibits SUV-induced skin carcinogenesis in mouse skin epidermal tissue. Dorsal trunk skin samples were harvested and stained with H&E (left panels) or with an antibody to detect PCNA (right panels). Representative staining shows the pathologic changes in the epidermis from each of the groups (scale bar = 100 μm). Expression of PCNA was quantified using Image-Pro Plus software and stained cells were counted from 5 separate areas on each slide (lower panel). An average of 3 samples was calculated per group. Data are expressed as mean percent of control ± S.D. and the asterisks indicate a significant difference in PCNA expression (***, p < 0.001). E, ADA-07 inhibits SUV-induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2, p38, and JNKs in mouse skin. The expression levels of phosphorylated and total proteins were analyzed by Western blot.