Fig. 4.
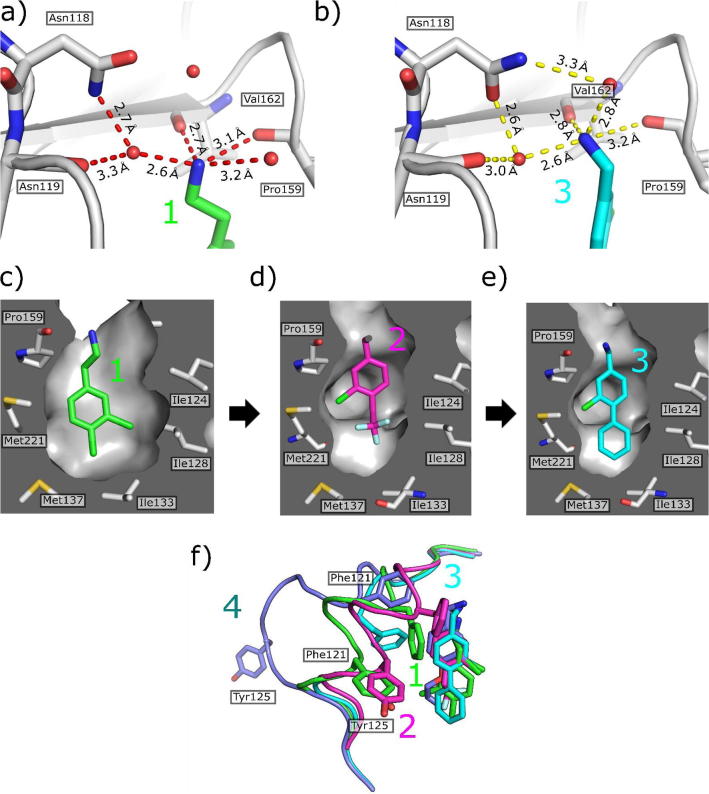
The optimisation of the αD site fragment. a) The interactions of the amine of 1 with the backbone carbonyls of Val162 and Pro159 along with the interaction with Asn118 and Asn119 via a water bridge (PDB: 5CLP). b) The interactions of the amine of 7 with the backbone carbonyls of Val162 and Pro159 along with the interaction with Asn118 and Asn119 via a water bridge (PDB: 5CHS). Since the amine of 7 sits higher up in the pocket, it pulls down the top water into hydrogen bonding distance, thereby forming another water bridge to Asn118. c) The hydrophobic core of 1 sits in the hydrophobic pocket of the αD site (PDB: 5CLP), however there is still potential to optimise the interactions with this pocket. d) From the crystal structure it appears that 2 is more selective for the αD site over the ATP site, however, the OCF3 group does not fill the hydrophobic pocket of the αD site (PDB: 5CVF). e) The crystal structure of 7 bound in the αD site shows that the molecule fills the hydrophobic core of the αD pocket more efficiently (PDB: 5CHS). f) Movement of the αD loop upon binding of compounds 1 (green), 2 (magenta), 3 (cyan) and 4 (light blue).