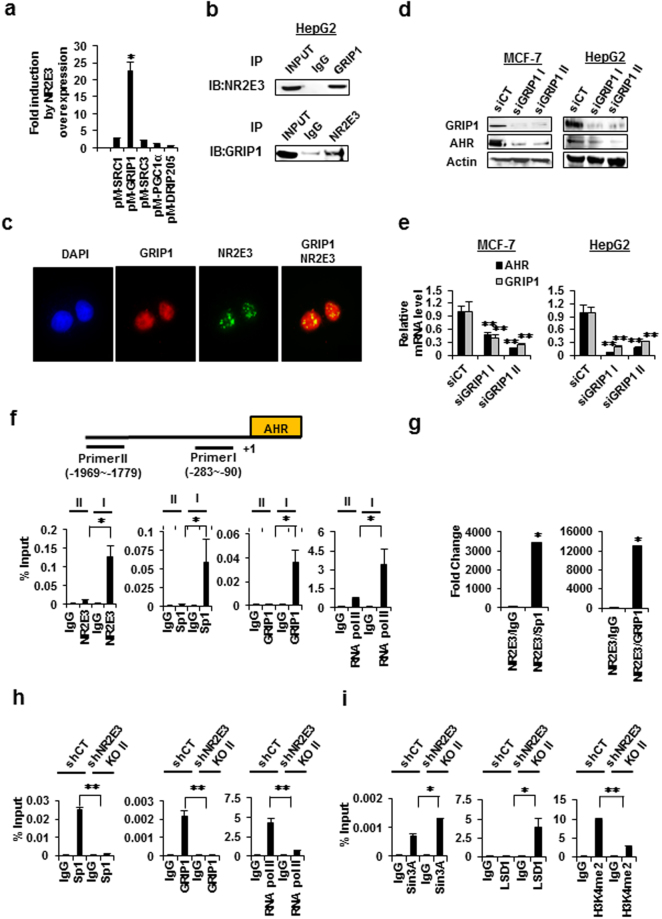
Figure 3.
Formation of transcriptionally active complexes between NR2E3, Sp1, and GRIP1 on the proximal region of the AHR gene promoter. (a) Effects of NR2E3 overexpression on the GAL4 reporter luciferase activity in cells co-transfected with pM vector containing GAL4 DBD-linked coactivator, including SRC1, GRIP1 (SRC2), SRC3, PGC1α, and DRIP205 (TRAP220). (b) Co-IP assays confirmed the interactions between NR2E3 and GRIP1. HepG2 cells were lysed and Co-Immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed with anti-GRIP1 antibody or control non-immune IgG (IgG), followed by immunoblot analysis (IB) with NR2E3 antibody (Top). A reciprocal Co-IP assay with opposite set of antibodies was also performed (Bottom). (c) Co-localization of NR2E3 with GRIP1 in the nucleus of HepG2 cells. (d,e) Effect of GRIP1 depletion by using small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) targeting GRIP1 (siGRIP1 I and II) and scrambled control (siCT) on AHR and GRIP1 protein expression and mRNA levels in MCF-7 and HepG2 cells. (f) Binding of NR2E3, Sp1, and GRIP1 and RNA polymerase II on the AHR promoter regions, distal (−1969 to −1779) and proximal (−283 to −90) in HepG2 cells, as determined by ChIP-PCR. (g) Re-ChIP analysis of the complex formation between NR2E3 and Sp1 or NR2E3 and GRIP1 on the AHR proximal promoter region in HepG2 cells. (h,i) Effects of NR2E3 loss on the transcriptional and epigenetic status of the AHR proximal promoter. Binding of Sp1, GRIP1, RNA pol II, and H3K4me2 were reduced whereas binding of the corepressors Sin3A and LSD1 was increased. Results are means ± SE for at least two or three independent experiments with three replicates per experiment, and significantly (P < 0.05) increased (*) or reduced (**) responses are indicated.