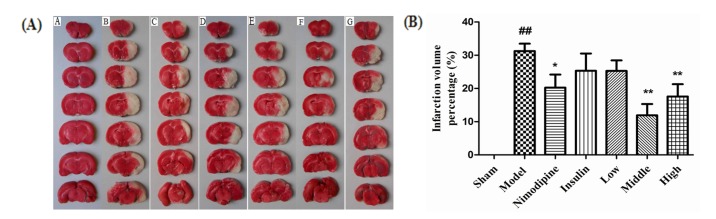
Fig. 2. Effect of rhGLP-1 (7-36) on the infarction volumes of MCAO/R diabetic rats.
(A) Typical TTC stained brain slices of MCAO/R rats in different groups. The normal brain tissue is red and the cerebral ischemia and infarction tissues are white (n=6). A, Sham group; B, Model group; C, Nimodipine group; D, Insulin group; E, Low-rhGLP-1 (7-36) group; F, Middle-rhGLP-1 (7-36) group; G, High-rhGLP-1 (7-36) group. (B) Infarction volume percentage of MCAO/R rats in different groups, columns represent the Mean±S.E.M (n=6). Infarction volumes were measured at 72h after administration, rhGLP-1 (7-36) (20, 40 µg/kg ip, tid) and nimodipine (0.5 mg/kg ip, qd) can significantly reduced Infarction volumes compared to the Model group. The intergroup variation was analyzed by ANOVA followed by LSD test. ##p<0.01 vs. Sham group; *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs. Model group.