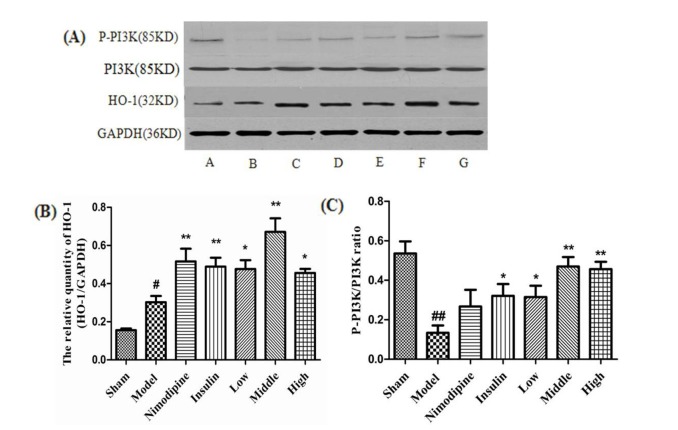
Fig. 6. Effect of rhGLP-1 on the levels of HO-1 expression and P-PI3K/PI3K ratio in the cerebral cortex of the ischemia-reperfusion damage.
(A) Expressions of HO-1 and P-PI3K protein in MCAO/R rats in different groups (n=4) with GAPDH as a loading control. A, Sham group; B, Model group; C, Nimodipine group; D, Insulin group; E, Low-rhGLP-1 (7-36) group; F, Middle-rhGLP-1 (7-36) group; G, High-rhGLP-1 (7-36) group. (B) HO-1/GAPDH in different groups (Mean±S.E.M, n=4). At 72 h after administration, compared with the Model group, rhGLP-1 (7-36) (10, 20, 40 µg/kg ip, tid), nimodipine (0.5 mg/kg ip, qd) and insulin (0~1 IU/kg ip, bid) can significantly enhance HO-1 protein expression. The intergroup variation was analyzed by ANOVA followed by LSD test. #p<0.05 vs. Sham group; *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs. Model group. (C) P-PI3K/PI3K ratio in different groups (Mean±S.E.M, n=4). At 72 h after administration, compared with the Model group, rhGLP-1 (7-36) (10, 20, 40 µg/kg ip, tid) and insulin (0~1 IU/kg ip, bid) can significantly enhance P-PI3K/PI3K ratio. The intergroup variation was analyzed by ANOVA followed by LSD test. ##p<0.01 vs. Sham group; *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs. Model group.