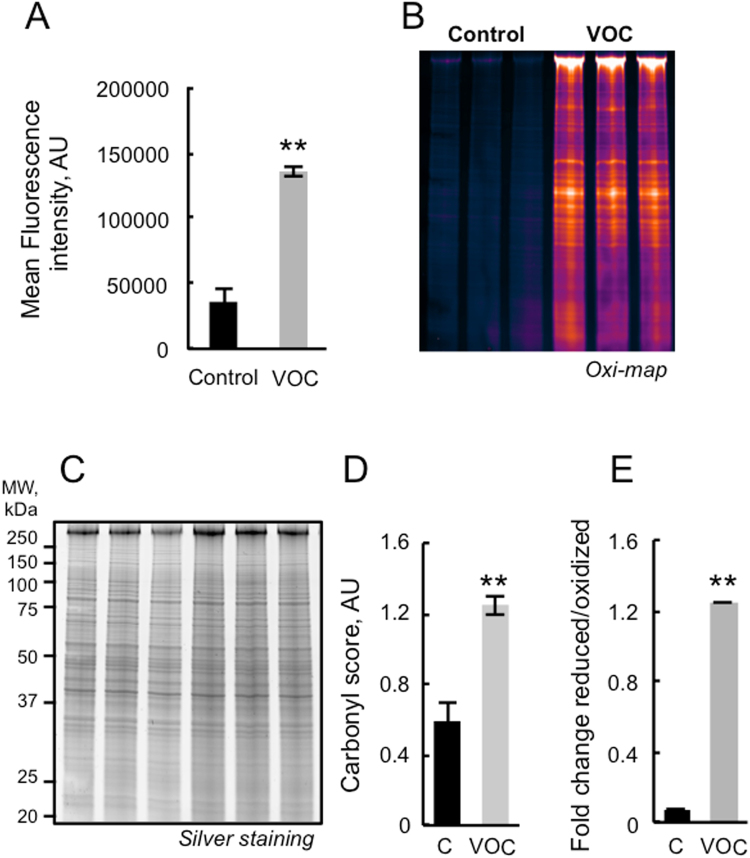
Figure 4.
Detection of oxidatively modified proteins and lipid peroxidation following VOC exposure. (A) Primary keratinocytes were exposed to VOCs (toluene, hexane, acetaldehyde, formaldehyde, acetone, 20 ppmV, each) for 4 hours. After 24 hours, carbonylated protein within cells was evaluated by flow cytometry using cells stained with Anti-FITC conjugated monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to DNP moiety. Results are presented as the mean fluorescent intensity of the cells. Data, mean ± SEM from three independent cultures,** P < 0.01. (B) Fluorescent detection of oxidized proteins. Keratinocytes were exposed to the same cocktail of VOCs. After 24 hours, cells were analyzed by SDS-PAGE (4–20%) pattern of carbonylated proteins pre-labeled with C5Hz (Cy5 hydrazine labeling). The gel was cropped and full-length gel is included in Supplementary file information. (C) Total proteins post-stained with Protein GOLDTM. The gel was cropped and full-length gel is included in Supplementary file information. (D) Semi-quantification of carbonylated proteins were performed by densitometric analysis, expressed as relative values and shown as mean ± S.D (n = 3) and analyzed using Student’s t-test; **P < 0.01. (E) Lipid peroxidation detection with Image-iT Peroxidation Kit. Visualization of lipid peroxidation in-situ was carried out through labeling cells with C11-BODIPY581/591, a fatty acid analogue that readily incorporates into cell membranes and whose fluorescence irreversibly changes from red to green upon exposure to ROS. Keratinocytes were stained with 10 µM C11-BODIPY581/591for 30 minutes, exposed to VOCs and analyzed after treatment with a microplate fluorimetric reader. In control cells, most of the signal is in the red channel and the ratio of 590/510 (reduced/oxidized) is high. Data, mean ± SEM from three independent cultures, **P < 0.01.