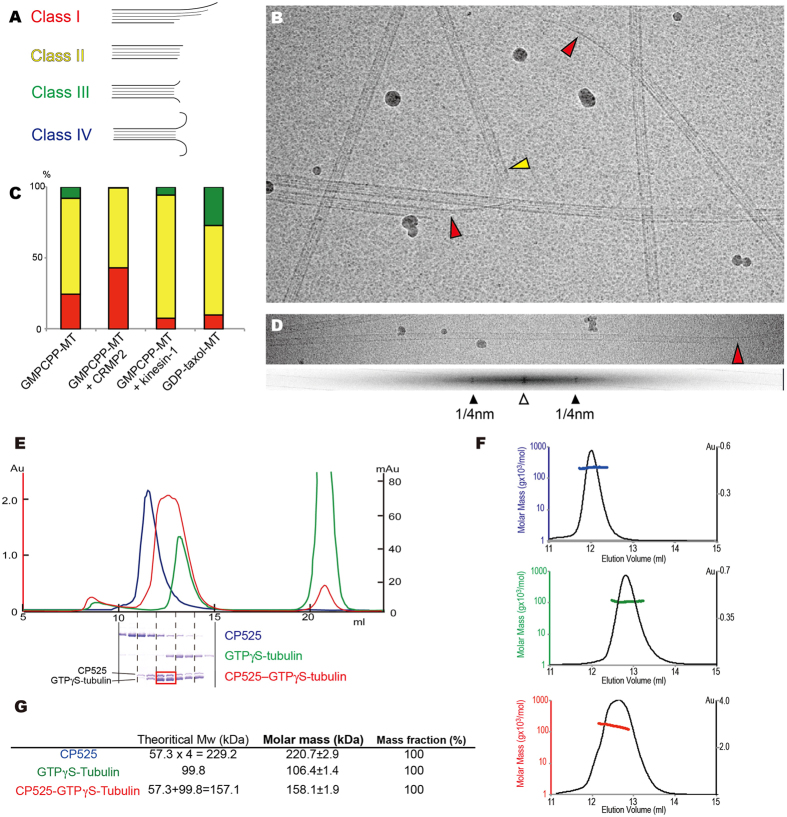
Figure 3.
CRMP2 induces GTP-state microtubules through the interaction with soluble GTP-tubulin dimer. (A) Classification of microtubule ends. I, curved sheets; II, blunt ends; III, tapered ends; IV, curved ends. (B) Representative examples for end shapes of GMPCPP-microtubules in the presence of CP525. Red and yellow arrows show class I and class II ends, respectively. (C) Percentage of end types observed. GMPCPP-microtubule (n = 187); GMPCPP-microtubule+CP525 (n = 184); GMPCPP-microtubule+kinesin-1 (nucleotide free) (n = 230); GDP-taxol-microtubule (n = 205). (D) Cryo-EM image of CP525-induced GMPCPP microtubule (top) and its FFT image (bottom) are displayed. (E) Size exclusion chromatography of CP525 (blue), GTP-γS-tubulin-dimer (green), and CP525 with GTP-γS-tubulin-dimer (red) shown with SDS-PAGE results. (F) SEC-MALS analyses of CP525 (top), GTP-γS-tubulin (middle) and their mixture (bottom). (G) The molar mass determined by SEC-MALS experiments. Theoretical molecular weights calculated from the amino acid sequence were also shown for comparison.