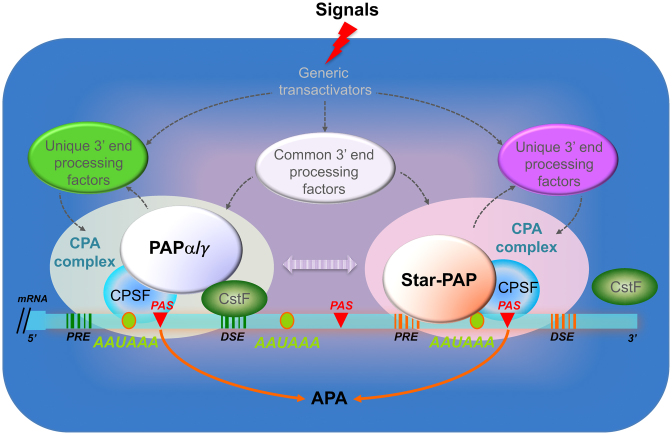
Figure 6.
Model of APA regulation by the nuclear non-canonical and canonical PAPs. Cellular signals stimulate certain transactivators, which further activate specific 3′ end processing factors that selectively integrate into distinct mRNA 3′ end cleavage and polyadenylation (CPA) complexes for the activation of Star-PAP or the canonical PAPs. The PAP recognition element (PRE) upstream of PAS serves as a docking site for specific RNA-binding proteins including Star-PAP. In contrast, recruitment of PAPα or PAPγ to the CPA complex requires CstF64 binding to the downstream sequence element (DSE) and its interaction with the CPSF processing factors. Substitution of a specific PAP within an mRNA 3′ end processing complex by another PAP could potentially be permissible for the processing of certain but not all target genes. Solid arrows indicate direct regulation; dotted arrows represent observations from previous studies or suggested regulatory mechanisms.