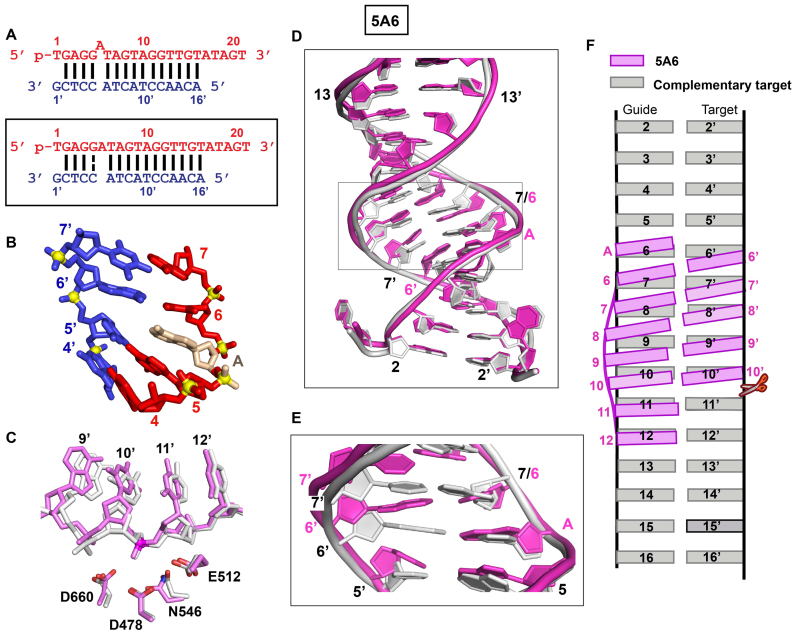
Figure 2.
Crystal structures of TtAgo (TtAgo D546N catalytic mutant) bound to 5′-phosphorylated 22-nt guide DNA and 19-nt target DNA containing a 5A6 bulge positioned on the guide strand within the seed segment and conformational adjustments on proceeding from control to 5A6 bulge-containing ternary complexes. (A) Sequence of the guide DNA–target DNA duplex (top panel), with the actual alignment of the bulge in the crystal structure of the ternary complex (bottom boxed panel), where an adenine stacks into the duplex between positions 5 and 6 of the guide strand. (B) A stick representation of the bulge site and two flanking base pairs, with the stacked- in adenine highlighted in biscuit color in the 2.8 Å structure of the 5A6 bulge-containing ternary complex. There are two molecules of the complex in the asymmetric unit and the 3′-end of the guide strand is inserted into the PAZ pocket of an adjacent molecule in the crystal lattice (not shown). (C) The positioning of the DNA target strand of the control containing no bulge (in silver) and in the 5A6 bulge (in magenta) relative to the catalytic residues (D478, D660, E512 and D546N mutant) of the RNase H fold of the PIWI domain in the TtAgo ternary complexes. The catalytic residues are equidistant from the phosphate linking the 10’–11’ step (colored in red) in the control (in silver) and 5A6 bulge (in magenta)-containing Ago ternary complexes. (D, E) Superposition of the seed and cleavage site segments of the guide-target duplex in the no-bulge control (in silver) and 5A6 bulge-containing (in magenta) Ago ternary complexes. The segment spans 1–1’ to 14–14’ in panel D and spans 5–5′ to 8–8’ in panel E. (F) Schematic emphasizing base tilting of the guide strand between 5–5′ and 11–11’ pairs in the duplex of the 5A6 bulge-containing Ago ternary complex (in magenta), relative to the duplex of the no-bulge control ternary complex (in silver).