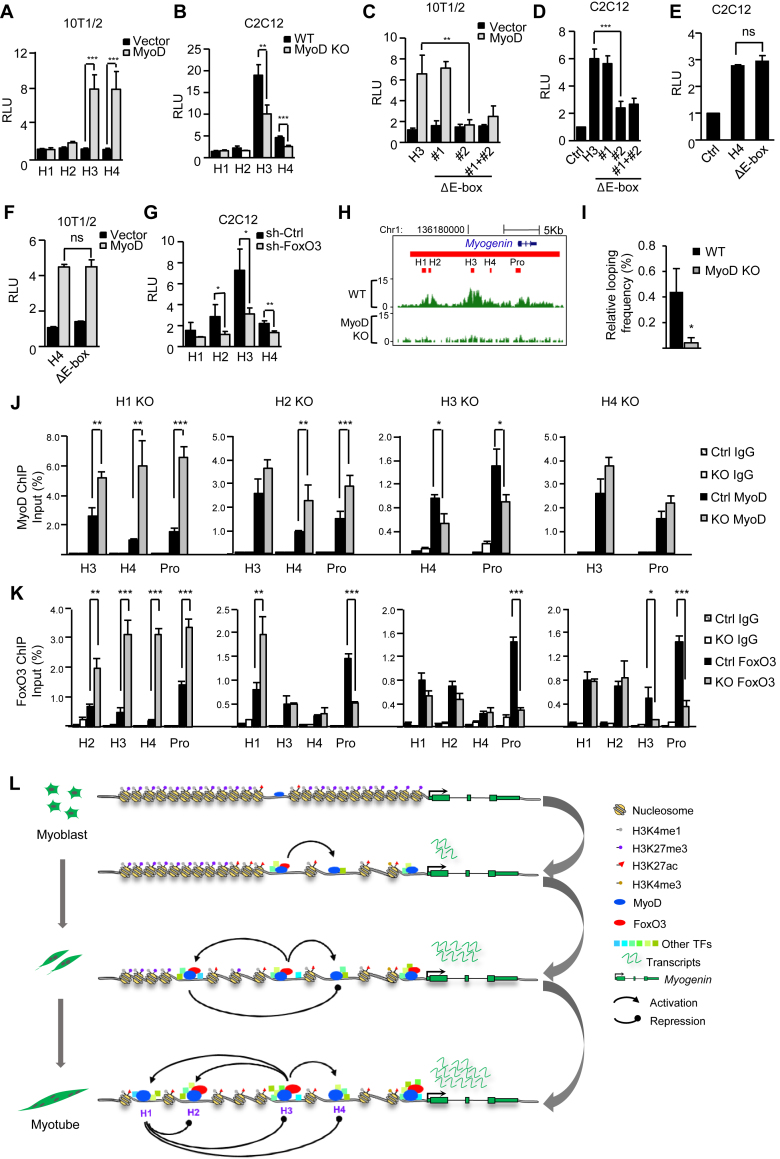
Figure 6.
MyoD and FoxO3 orchestrate the hotspot interactions. (A) Overexpression of MyoD in 10T1/2 cells induced the H3 or H4 hotspot reporter activities. (B) H3 or H4 reporter activity was decreased in MyoD KO cells. (C) Deletion of motif # 2 or both but not #1 diminished the induction of H3 reporter by MyoD overexpression in 10T1/2 cells. (D) The deletion of motif # 2 or both but not #1 diminished the H3 reporter activities in differentiating C2C12 MTs. (E) Deletion of the motif in H4 had no impact on H4 reporter activity in differentiating C2C12 MTs. ns, no significance. (F) The deletion of the motif had no impact on the induction of H4 activity by MyoD over-expression in 10T1/2 cells. (G) H2, H3 or H4 hotspot reporter activity was reduced in shFoxO3 MTs compared to the vector control. (H) H3K27ac ChIP-seq was performed in WT or MyoD KO cells to assess the impact of MyoD deletion on hotspot activity. (I) The interaction between H3 and H4 was decreased in MyoD KO cells as assessed by 3C-PCR. (J and K) The impact of each hotspot deletion on the enrichment of MyoD or FoxO3 on the hotspots and Myogenin promoter was examined by ChIP-PCR. All luciferase data were normalized to Renillia protein and represent the average of three independent experiments ± s.d. Relative Luciferase Unit (RLU) normalized to the vector or WT control is shown. All qRT-PCR and ChIP-PCR data were normalized to GAPDH mRNA and ChIP input respectively and represent the average of three independent experiments ±s.d. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001. (L) Schematic illustration of MyoD/FoxO3 mediated hotspot interaction that orchestrates Myogenin SE activation during MB differentiation. The dominant H3 hotspot is primed in the MB by MyoD binding; upon early differentiation, binding of FoxO3 further amplifies its activity and subsequent interaction with H4; H3 next interacts with H2 and H1 to activate their formation; H1 appears to repress the other three hotspots thus acting as a brake. Altogether the hierarchical activation of the four hotspots orchestrates the Myogenin gene expression.