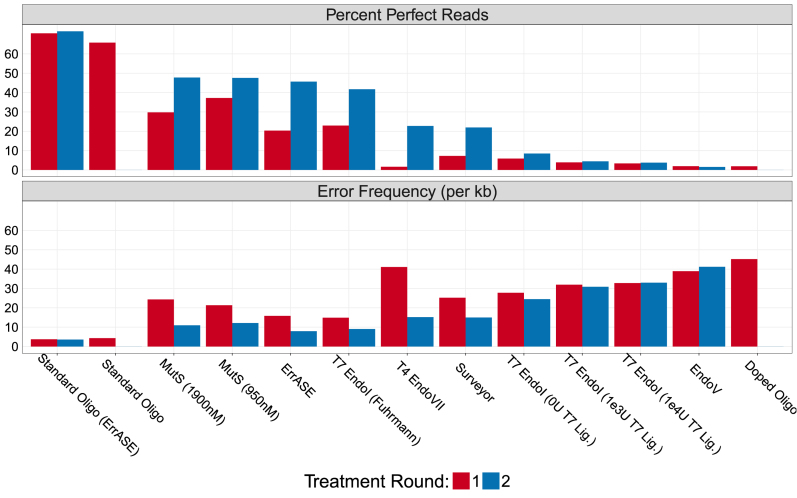
Figure 3.
Effectiveness of enzymatic error correction methods. Here, we compare the error frequency (errors/kb) and number of perfect assemblies for 10 different enzymatic error correction methods. We find that MutS is the most effective enzyme at increasing the percentage of perfect assemblies. However, ErrASE is the most effective at decreasing error frequency. Additionally, we see that the efficacy of T7 Endonuclease I and MutS are dependent on protocol, and that the addition of a ligase had detrimental effects on sequence quality. Note: the x-axis is ordered by decreasing number of perfect assemblies.