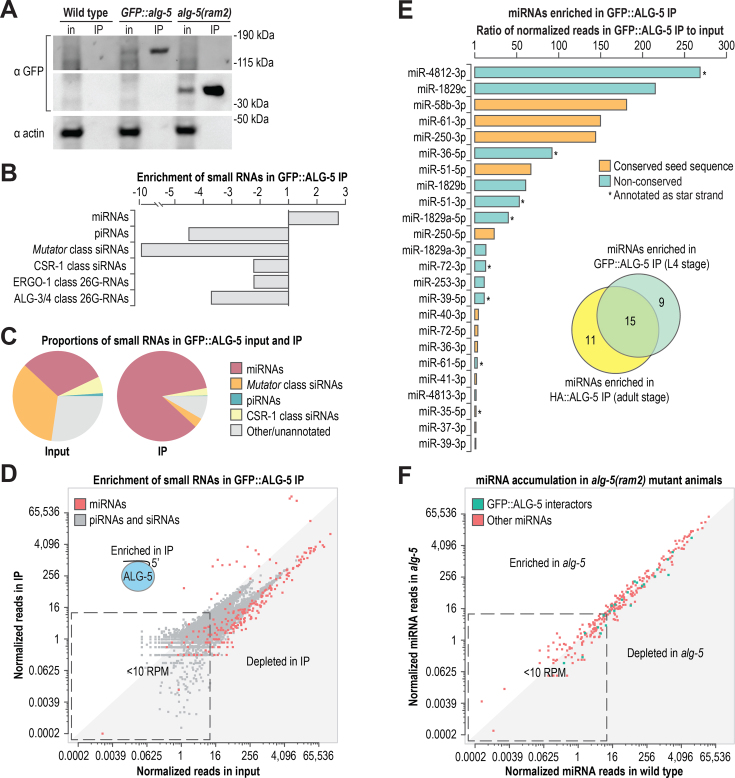
Figure 3.
ALG-5 binds a subset of miRNAs. (A) Western blot assay of GFP::ALG-5 from cell lysates (input, in) and co-IPs (IP) used for small RNA isolation and sequencing. Wild type and alg-5(ram2) were included as controls. ∼0.2% starting material equivalents for the input fractions and ∼5% starting material equivalents for the co-IP fractions were run on the gels for western blots. (B) Enrichment of miRNAs, piRNAs, and siRNAs in GFP::ALG-5 co-IP relative to input as determined by high-throughput sequencing. (C) The relative proportions of each class of small RNAs in input and co-IP fractions. (D) Normalized reads (reads per million total mapped reads) for each miRNA in GFP::ALG-5 co-IP versus input are shown in red. Normalized reads for other classes of small RNAs (piRNAs and siRNA loci) are shown in gray. (E) miRNAs enriched >1-fold in the GFP::ALG-5 co-IP relative to input. Colors indicate if the seed sequence (positions 2–8) is conserved in Drosophila melanogaster and/or Homo sapiens. Asterisks indicate if the sequence is annotated as a star strand in miRBase v. 20. The inset Venn diagram displays the overlap in miRNAs enriched in the GFP::ALG-5 (L4 stage animals) and HA::ALG-5 (adult animals) co-IPs. (F) Normalized reads for each miRNA in alg-5(ram2) versus wild type. See also Supplementary Figure S3 and Tables S3–S5.