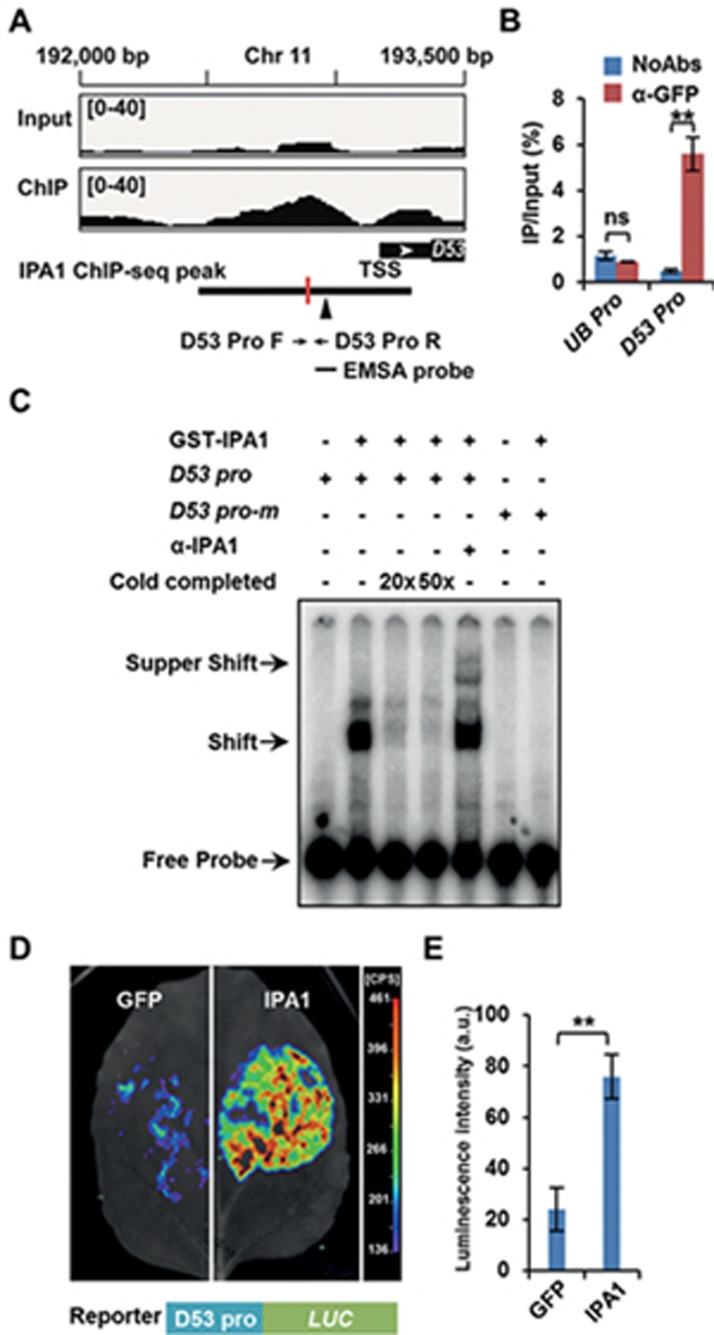
Figure 5.
IPA1 binds to the D53 promoter and regulates D53 expression. (A) IPA1 binding profile in the promoter of D53. The solid arrowhead refers to the GTAC around the peak summit, and red vertical line to peak summit. Primer pairs D53-ProF and D53-ProR (Supplementary information, Table S1) were used for ChIP-qPCR. The probe was used in EMSA. TSS, transcription start site. (B) Validation of IPA1 direct binding sites in the D53 promoter by ChIP-qPCR analysis. Values are means ± sem (n = 3). The double asterisk represents significant difference determined by the Student's t test at P < 0.01; ns, no significant difference. (C) Direct binding of IPA1 to the D53 promoter in the EMSA assay. The 20- and 50-fold excess non-labeled probes were used for competition. The D53 pro-m is a mutated version of D53 pro probe with the SBP binding motif GTAC changing to ATAC. (D) Transcriptional activity assay in tobacco leaf, showing that IPA1 could enhance the expression of the D53 promoter-drived LUC reporter. A. tumefaciens transformed with Pro35S:IPA1-MYC, Pro35S:GFP, and ProD53:LUC were mixed and injected into tobacco leaves. D-luciferin was used as the substrate of Luciferase. (E) Statistical analysis of (D). Values are means ± SD (n = 3). The asterisk represents significant difference determined by Student's t test. **P < 0.01.