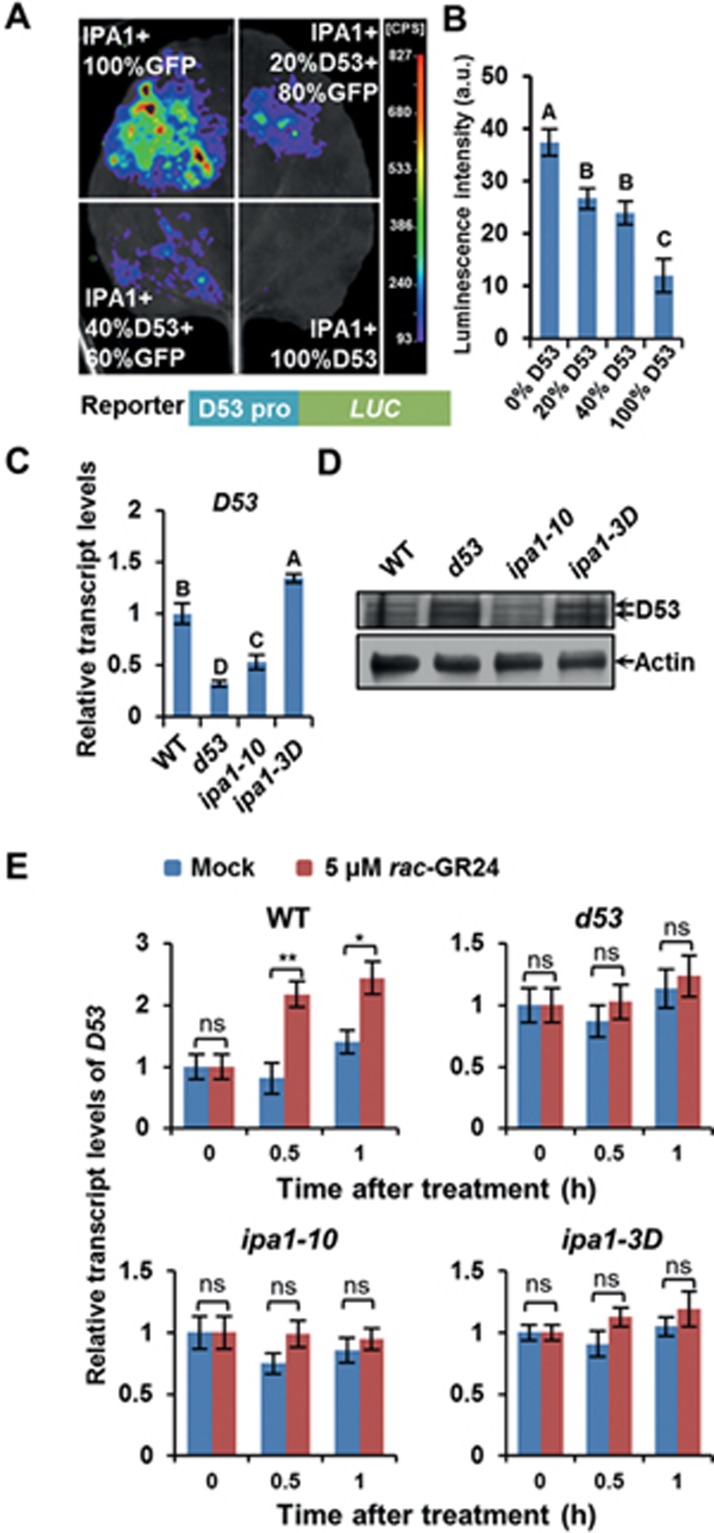
Figure 6.
D53 and IPA1 form a feedback regulation loop in SL signaling. (A) Transcriptional activity assay in tobacco, showing that D53 represses the IPA1-drived activation of the D53 promoter. A. tumefaciens transformed with Pro35S:IPA1-MYC, Pro35S:GFP, ProD53:LUC, and Pro35S:FLAG-D53 were mixed and injected into tobacco leaves. D-luciferin was used as the substrate of LUC. (B) Statistical analysis of (A). Values are means ± SD (n = 3). Different letters at top of each column indicate a significant difference at P < 0.05 determined by Tukey's HSD test. (C) D53 transcript levels in WT, d53 and ipa1 mutants. Values are means ± sem (n = 3). Different letters at top of each column indicate a significant difference at P < 0.05 determined by Tukey's HSD test. (D) D53 protein levels in WT, d53 and ipa1 mutants. D53 was detected by rabbit polyclonal antibodies anti-D53. Actin was used as the loading control. (E) Mutations in IPA1 disrupt SL-induced D53 transcription after rac-GR24 treatment. Values are means ± sem (n = 3). Statistical differences between mock and treatment at same time points were determined by Student's t test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; ns, no significant difference.