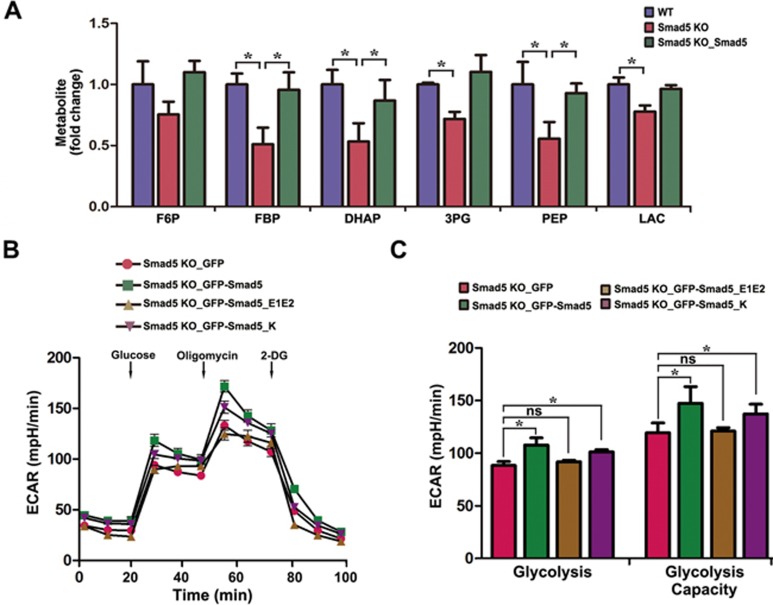
Figure 4.
Loss of function of Smad5 causes glycolysis defects. (A) LC-MS/MS analysis of abundance in glycolytic intermediates in WT, Smad5 KO and Smad5 pre-rescue hES cells. Data are represented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. Unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test. *P < 0.05. (B) GFP, GFP-Smad5, GFP-Smad5_E1E2 and GFP-Smad5_K were expressed in Smad5 KO HEK293 cells, and extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) was measured with the Seahorse Analyzer (n = 6). (C) Statistics of glycolysis and glycolysis capacity in B. Data are represented as mean ± SEM of six independent experiments. Unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test. *P < 0.05.