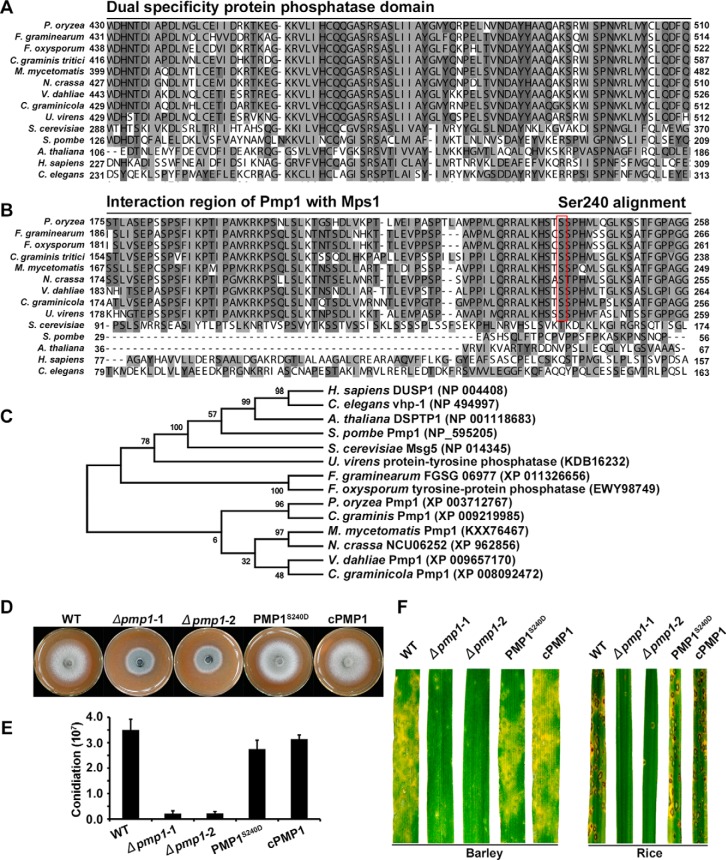
Fig. 4.
Functional characterization of Pmp1. Alignments of the dual specificity domain (A) and the interaction region of Pmp1 (B) from P. oryzae with orthologs from other organisms were performed using the ClustalX program. C, A phylogenetic tree of Pmp1 orthologs, generated by the MEGA7 program, with 500 bootstraps. The sequences of dual specificity protein phosphatase families were from organisms as follows: Pyricularia oryzae Pmp1 (XP_003712767), Madurella mycetomatis Pmp1 (KXX76467), Neurospora crassa NCU06252 (XP_962856), Gaeumannomyces graminis Pmp1 (XP_009219985), Fusarium graminearum FGSG_06977 (XP_011326656), Verticillium dahlia Pmp1 (XP_009657170), Colletotrichum graminicola dual specificity phosphatase (XP_008092472), Fusarium oxysporum tyrosine-protein phosphatase (EWY98749), Ustilaginoidea virens protein-tyrosine phosphatase (KDB16232), Homo sapiens DUSP1 (NP_004408), Schizosaccharomyces pombe Pmp1 (NP_595205), Saccharomyces cerevisiae MSG5 (NP_014345), Arabidopsis thaliana DSPTP1 (NP_001118683), Caenorhabditis elegans vhp-1 (NP_494997). D, Colony growth of wild-type strain P131 (WT), pmp1 deletion mutants (Δpmp1-1 and Δpmp1-2), PmpS240D allele transformant and complemented strain cPmp1 on OTA medium for 5 days. E, Conidiation of the same set of strains. F, Lesions formed by the same set of strains on barley (Left) and rice (right) leaves. Barley and rice seedlings were sprayed with conidial suspensions, and cultured for 5 days and 7 days, respectively.