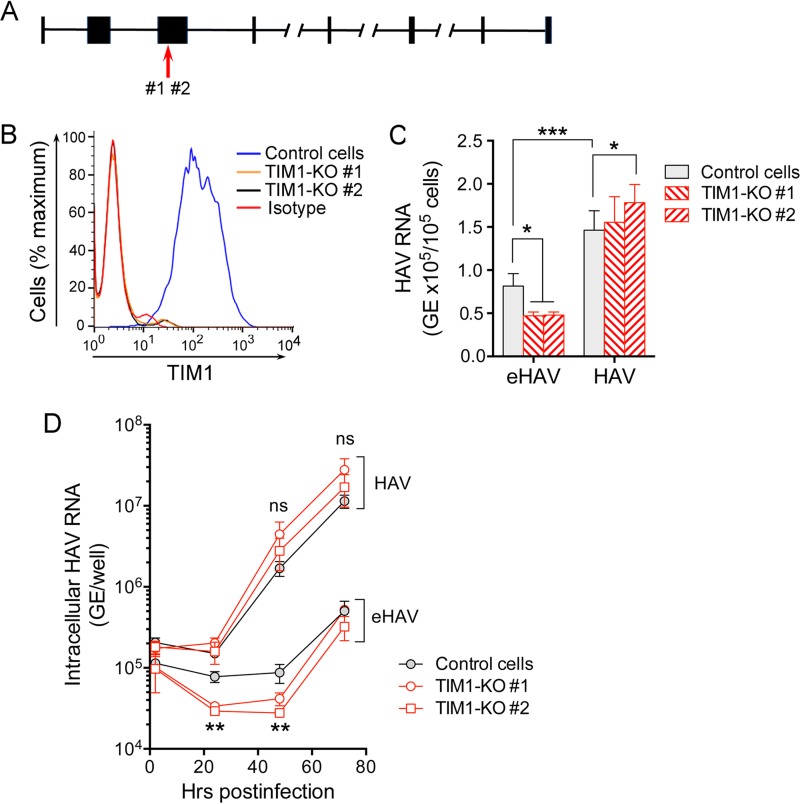
FIG 2 .
Impact of TIM1 knockout on HAV infection of Vero cells. (A) African green monkey HAVCR1 gene structure (NCBI Chlorocebus sabaeus annotation release 100, accession no. XM_008015132.1; map not drawn to scale). The red arrow shows the location of CRISPR-induced disruption of the TIM1 sequence in exon 3 as determined by DNA sequencing. (B) Expression of TIM1 on the surfaces of control and TIM1-KO Vero cells quantified by flow cytometry. “Isotype” refers to the immunoglobulin control. (C) Adherence of HAV and eHAV to Vero control and two distinct TIM1-KO cell lines at 4°C, determined by RT-qPCR specific for viral RNA. Error bars = SEM; n = 5 (2 independent experiments, each with 2-3 technical replicates). *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001. (D) Accumulation of intracellular HAV RNA in control and TIM1-KO Vero cells following infection at 37°C with eHAV or HAV inocula containing similar amounts of HAV RNA. Viral RNA in quasi-enveloped eHAV-infected control cells exceeded that in TIM1-KO cells at 24 and 48 h (TIM1-KO#1 [P < 0.05] and TIM1-KO#2 [P < 0.01] by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test). Error bars = SEM; n = 4 (2 independent experiments each with 2 technical replicates). There was no significant difference (ns) between HAV RNA levels in control and KO cell lines infected with naked HAV.