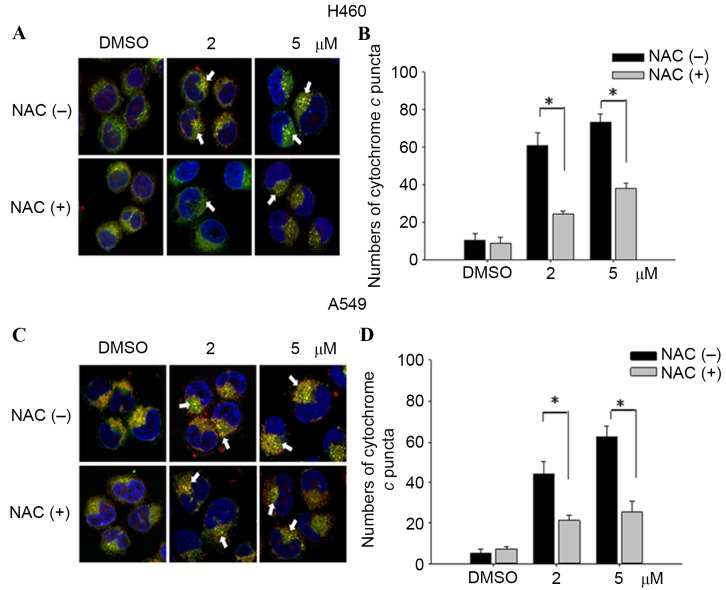
Figure 5.
Cytochrome c release in NSCLC cells. The release of cytochrome c was reduced from mitochondria in H460 and A549 cells pretreated with NAC (10 µM) for 1 h, followed by incubation with 2/5 µM teroxirone or the vehicle control (0.2% DMSO) for 24 h. Cells were fixed with 4% of formaldehyde, permeabilized and stained with an anti-cytochrome c antibody (dilution, 1:200) at 4°C for 18 h. Subsequent to washing, cells were stained with Mitotracker Green (mitochondrial staining), DAPI (nuclear staining) and secondary antibody conjugated with TRITC for cytochrome c. The pointed arrow signified the co-localization of cytochrome c (red) and mitochondria (green), whereas the nucleus is stained blue (scale bar, 100 µm). The release of cytochrome c punctae was quantified in H460 (A and B) and A549 (C and D) cells using ImageJ software. The results in the presence of NAC (+) and absence NAC (−) were compared. *P<0.05 vs. DMSO control. ROS, reactive oxygen species; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer cells; TRITC, tetramethylrhodamine; NAC, N-acetylcysteine; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide.