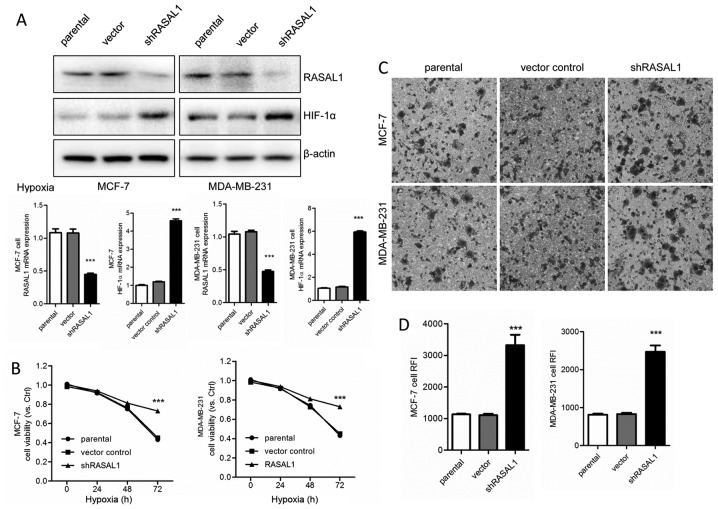
Figure 3.
Knockdown of RASAL1 in breast cancer cell lines ameliorates hypoxic cell viability and cell invasion in vitro by increasing the protein levels of HIF-1α and intracellular levels of ROS. (A) MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells were transfected with RASAL1-specific or scramble shRNA lentivirus for 72 h. The expression of RASAL1 and HIF-1α mRNA and protein levels were measured by quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blot analysis. (B) Cell viability is shown as the fold change in viability from the normoxic control in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells treated with hypoxia for various times. (C) Repression of invasion ability following knockdown of RASAL1 in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells under hypoxia for 24 h was detected using a Transwell assay (magnification, ×100). (D) Intracellular ROS accumulation was detected using a dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate probe after 24 h of hypoxia treatment. Each bar represents the mean ± standard error of the mean. The results were reproduced in three independent experiments. ***P<0.001 vs. the control group. RASAL1, RAS protein activator-like 1; HIF-1α, hypoxia inducible factor-1α; ROS, reactive oxygen species; shRNA, short hairpin RNA; RFI, relative fluorescence intensity.