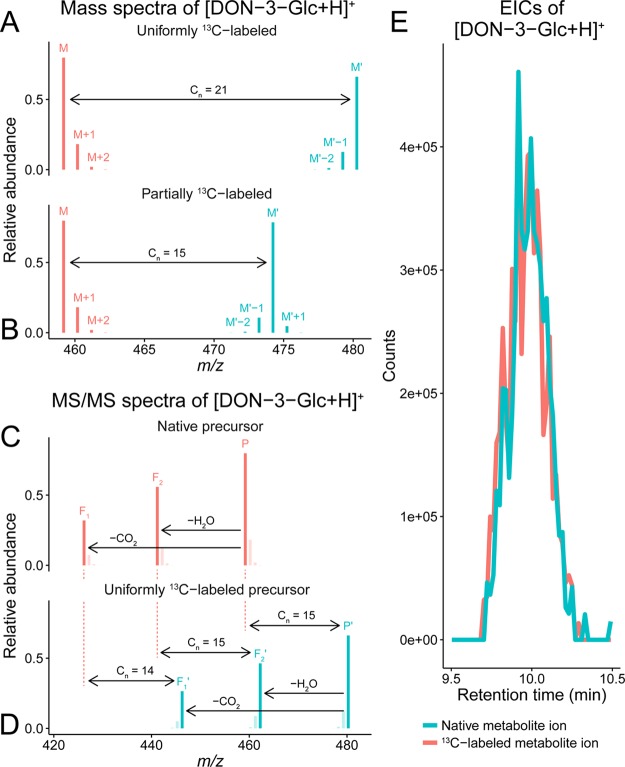
Figure 2.
LC-HRMS(/MS) data illustrating deoxynivalenol 3-glucoside (DON-3-Glc, C21H30O11). (A) Theoretical isotopologue patterns of native (M, [12C211H3016O11 + 1H]+; m/z 459.1862, native 12C enrichment of 98.93%) and U-13C-labeled (M′, [13C211H3016O11 + 1H]+; m/z 480.2566, uniform 13C enrichment of 99.1%) metabolite ions. Other isotopologue signals (e.g., 18O or 2H) are not depicted as their abundance is too low. (B) Isotope patterns of native and partly 13C-labeled (M′, [13C1512C61H3016O11 + 1H]+; m/z 474.2365) biotransformation product ions. In M′, only the 15 carbon atoms of DON are 13C, while the remaining six carbon atoms of Glc are 12C. The m/z difference (Δm) between M and M′ corresponds to the total number of labeled atoms in the respective ions (Cn). (C, D) Section of simulated MS/MS spectra of native and U-13C-labeled [DON-3-Glc + H]+ precursor ions. Mass increments between corresponding fragment ions (Fx and Fx′) reflect the number of 13C atoms per MS/MS fragment. Isotopologue signals of native and labeled precursor ions, as well as their fragments, will be present only if a corresponding broad mass isolation window is used in MS/MS analysis. (E) Coeluting chromatographic peaks of native and partly 13C-labeled [DON-3-Glc + H]+ (data provided by Kluger et al.).22