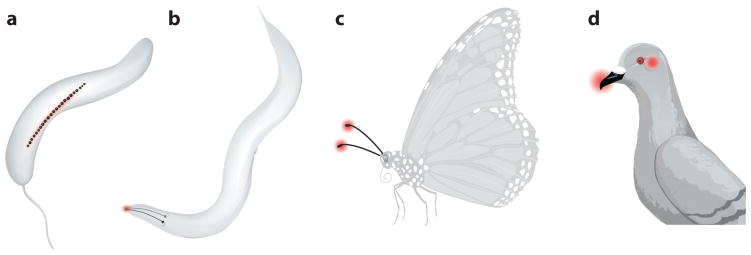
Figure 2.
Magnetosensory loci across organisms. Many organisms have been found to orient to the earth’s magnetic field with different sensory structures. (a) Magnetotactic bacteria use a micron-scale compass needle composed of a string of iron beads. (b) The nematode Caenorhabditis elegans uses the left-right pair of AFD sensory neurons that project sensory structures to the tip of the worm’s head. (c) Insects including butterflies and flies may use a cryptochrome-based chemical magnetic sensor in their antennae. (d) Birds may sense magnetic fields using magnetosensory cells in the inner ear and beak with an iron-based mechanism, and in eyes with a cryptochrome-based mechanism.