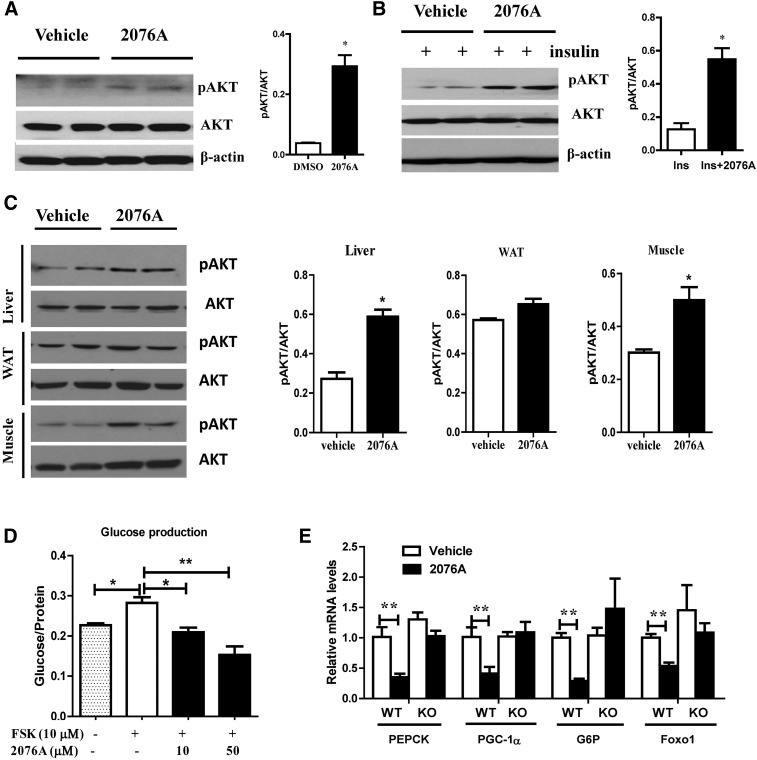
Fig. 7.
Treatment with 2076A sensitizes insulin signaling and inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis in vitro and in vivo. (A) Treatment of primary hepatocytes with 2076A increased the basal phosphorylation of Akt (p-AKT), as shown by Western blotting. Shown on the right is the densitometric quantification of the blots. (B) Treatment of primary hepatocytes with 2076A elevated the insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of Akt (p-AKT), as shown by Western blotting. Shown on the right is the densitometric quantification of the blots. (C) WT mice were treated with vehicle or 2076A (30 mg/kg per day) for 1 week before tissue harvesting and measurement of p-AKT in the liver, white adipose tissue, and skeletal muscle. Shown on the right is the densitometric quantification of the blots. (D) The inhibitory effect of 2076A on the forskolin-stimulated glucose production in primary hepatocytes isolated from WT mice. (E) The effect of 2076A on the hepatic expression of gluconeogenic genes in WT (n = 4) and FXR KO (n = 5) mice. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, compared with the vehicle-treated group.