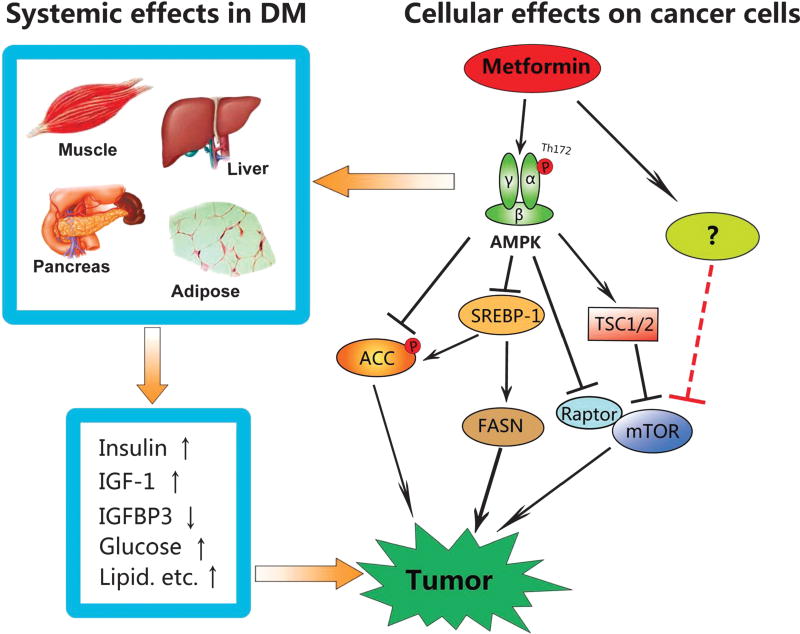
FIGURE 1.
Action of metformin on cancer. Two mechanisms are involved. First, in diabetes-associated cancer, metformin systemically ameliorates hyperinsulinemia, hypoglycemia, and hyperlipidemia, which are promoting factors not only for initiation of cancer, but also for progression of cancer. Second, at cellular levels, metformin activates AMPK, an immediate downstream effector of the tumor suppressor LKB1. Metformin inhibits the mTOR pathway through both AMPK-dependent and independent mechanisms. AMPK can also inhibit SREBP-1 by regulating its expression and phosphorylation, leading to down-regulation of FASN and acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC). In addition, AMPK directly phosphorylates and inhibits ACC. In summary, metformin suppresses de novo syntheses of fatty acids and protein synthesis in cancer cells.