Figure 5.
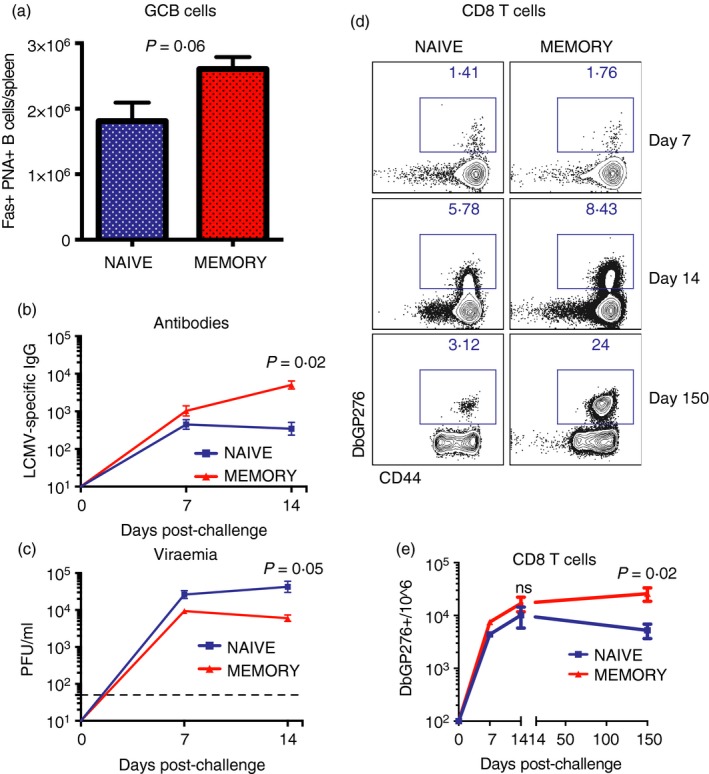
Memory CD4 T cells are more effective at helping B‐cell responses and sustaining CD8 T‐cell responses compared with naive CD4 T cells. (a) Summary of germinal centre (GC) B‐cell responses. (b) Summary of antibody responses. (c) Summary of viral control. (d) Representative FACS plots showing the frequencies of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) ‐specific CD8 T‐cell responses at various time‐points. (e) Summary of LCMV‐specific CD8 T‐cell responses. 106 naive or 106 memory SMARTA cells from spleen were transferred into different recipient mice, followed by LCMV Cl‐13 challenge 1 day after. (a) Spleen at day 14; (b, c) sera and (d, e) are from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). These experiments represent single SMARTA transfers (naive versus memory) to specifically assess their contribution to the immune response. Data are from two experiments, n = 4 or n = 5 mice/group per experiment. Error bars indicate SEM. [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
