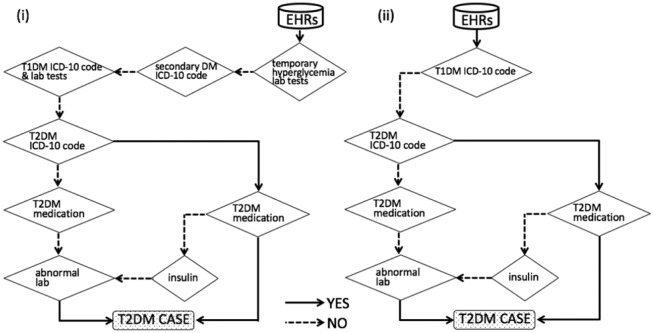
Figure 2.
(i) Modified PheKB algorithm (F), which is designed for high PPV. Algorithm (D) could include the obvious T2DM patients in accordance with the diagnosis criteria in Japan. This is also an aggressive strategy to specifically exclude T1DM, secondary DM, and temporary hyperglycemia. These points greatly differentiate (D) from (C). Abnormal lab indicates the following: a maximum value of random glucose ≥ 200 mg/dL and (1) a maximum value of HbA1c ≥ 6.5% or (2) a maximum value of HbA1c (J) ≥ 6.1%. T1DM lab tests are one of the following: (1) a maximum GAD-antibody value of ≥ 1.5 U/mL or (2) a maximum 125I-insulin biding ratio of ≥ 7% or (3) a maximum IA2-antibody value of ≥ 0.4 U/mL. The details of other steps are shown in Table 2. (ii) PheKB algorithm (G). Steps of T2DM Dx by physician ≥ 2, T2DM Rx precedes T1DM Rx, and diabetes medical supplies were excluded because they were data that were not included in the UT Hospital HL7 data. Abnormal lab means one of the following: (1) a maximum random glucose value of ≥ 200 mg/dL, (2) a maximum HbA1c of ≥ 6.5%, or (3) a maximum HbA1c (J) of ≥ 6.1%. The details of other steps are shown in Table 2.