Figure 8.
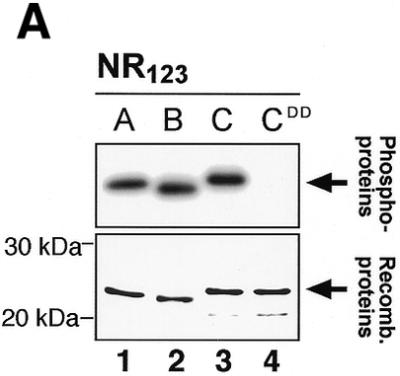
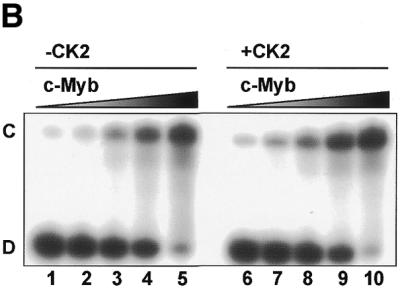
CK2 phosphorylation of A-, B- and c-Myb DBDs. (A) Recombinant NR123 domains of A-Myb (lane 1), B-Myb (lane 2), c-Myb (lane 3) and the S11D/S112D mutant of c-Myb (CDD; lane 4) were phosphorylated in vitro with [γ-32P]ATP and protein kinase CK2 at 30°C for 30 min before separation by SDS–PAGE and autoradiography (as described in Materials and Methods). The S11D/S12D mutant was constructed as previously described (22). The lower panel shows an SDS–PAGE analysis of the four NR123 domains from A-Myb (lane 1), B-Myb (lane 2), c-Myb (lane 3) and CDD (lane 4) (1.5 µg of each), purified as described, and visualized by staining with Coomassie brilliant blue. The theoretical molecular weights of the NR123 domains are 22.6, 22.0 and 23.1 kDa for A-, B- and c-Myb, respectively. (B) Recombinant NR123 domain of c-Myb (200 µg) was phosphorylated in vitro with 0.1 mM ATP (and trace amounts of [γ-32P]ATP) and protein kinase CK2 at 30°C for 30 min before separation on a SP Sepharose Fast Flow (Amersham Pharmacia) ion exchange column using a 150–1500 mM NaCl gradient. Equal amounts of non-phosphorylated NR123 domain of c-Myb and protein from the peak fraction corresponding to phosphorylated c-Myb were analysed by EMSA (as described in Materials and Methods). The degree of phosphorylation in the purified fraction was determined as described (75) and estimated to be 70%.
