Figure 2.
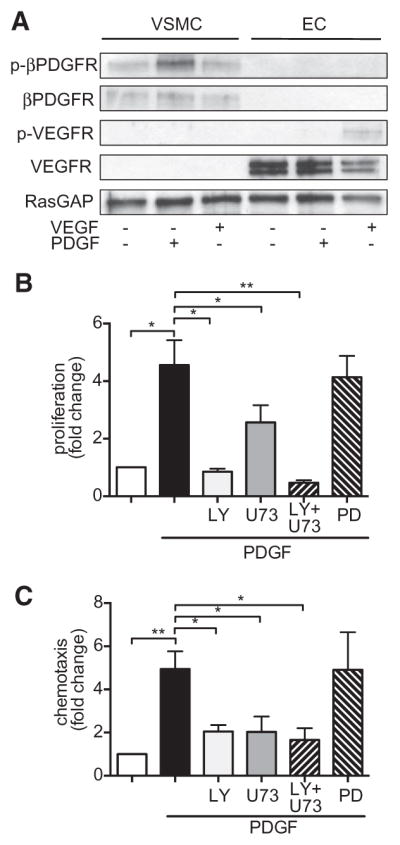
Critical role of platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR)–dependent activation of phophatidyl-inositol-3-kinase (PI3K) and phospholipase C-γ1 (PLCγ) in pulmonary hypertension. A, Expression of βPDGFR and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) and endothelial cells (EC), as well as activation (phosphorylation) of these receptors by platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF; 50 ng/mL) or VEGF (50 ng/mL) were assessed by western blot analyses. B and C, PDGF-dependent proliferation (B) and migration (C) of murine pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells were assessed as BrdU incorporation and by modified Boyden chamber assays, respectively. To assess the role of PI3K and PLCγ, cells were incubated with pharmacological inhibitors: The PI3K inhibitor LY294002 (LY, 10 mmol/L), the PLCγ inhibitor U73122 (U73, 10 mmol/L) or (as a control) the MEK kinase inhibitor PD98059 (PD, 5 mmol/L) 30 minutes before PDGF treatment. Furthermore, cells were treated with both PI3K and PLCγ inhibitors (LY+U73) followed by addition of PDGF. RasGAP indicates GTPase-activating protein of Ras. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
