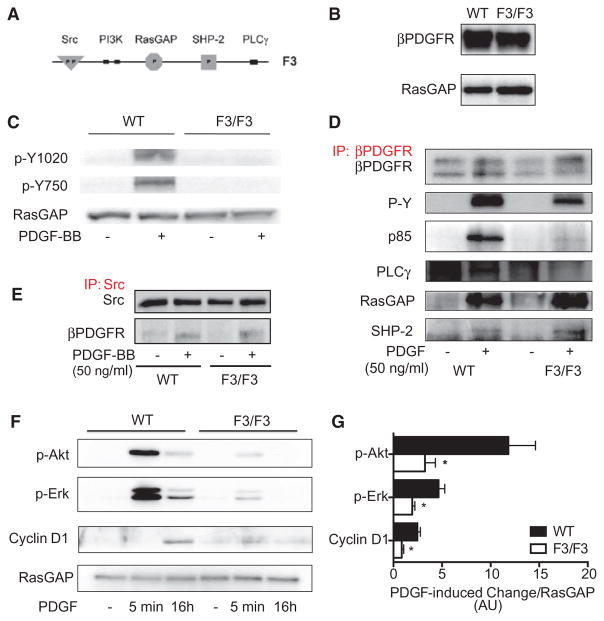
Figure 3.
Characterization of pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) isolated from wild-type (WT) and homozygous β platelet-derived growth factor receptor (βPDGFR)F3/F3 mice. A, Schematic diagram of the intracellular part of the βPDGFR F3 mutant showing lack of the tyrosine phosphorylation sites required for binding of phophatidyl-inositol-3-kinase (PI3K; Tyr-739/750) and phospholipase C-γ1 (PLCγ; Tyr-1020). B, Western blot analysis demonstrating equal protein expression levels of the βPDGFR in PASMC isolated from WT or βPDGFRF3/F3 mice (GTPase-activating protein of Ras [RasGAP] served as loading control). C, PASMC from WT or βPDGFRF3/F3 mice was treated with PDGF-BB or vehicle for 5 minutes. Phosphorylation of tyrosines Y1020 and Y750 was assessed by Western blot analysis using phospho- and site-specific antibodies. D, On treatment with PDGF-BB or vehicle, the βPDGFR was immunoprecipitated followed by Western blot analysis to detect total receptor phosphorylation (P-Y) or binding of associated signaling molecules (p85: regulatory subunit of PI3K, PLCγ, RasGAP, and SHP-2). E, To detect PDGF-dependent association of Src with the activated βPDGFR, Src was immunoprecipitated followed by detection of associated βPDGFR, cells treated as in (D). F and G, On stimulation with PDGF-BB or vehicle for the indicated time points, phosphorylation of Akt and Erk 1/2, as well as expression of the cell cycle protein cyclin D1 were assessed. Shown are a representative Western blot analysis (F) and the quantification by densitometry (G). AU indicates arbitrary units. *P<0.05.