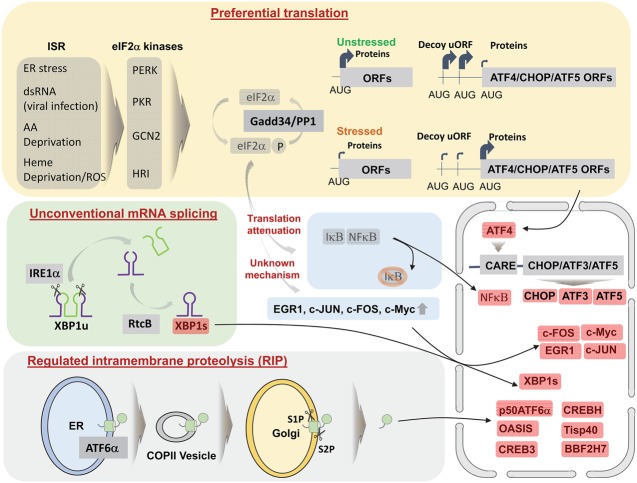
Figure 1.
Activation of TFs in the UPR. Upon stresses, activated eIF2α kinases phosphorylate eIF2α that is dephosphorylated Gadd34/PP1. Although phosphorylated eIF2α attenuates general mRNA translation, some TFs, including ATF4, CHOP, and ATF5, are preferentially translated. ATF4 then translocates into the nucleus to activate the promoter region harboring CARE motifs. During translational attenuation, IκB, an inhibitor of NF-κB, is depleted (due to its short half-life) to activate NF-κB. In addition, eIF2α phosphorylation induces some TFs involved in the immediate early response, including EGR1, c-JUN, c-FOS, and c-Myc, through an unknown mechanism. XBP1 mRNA cleaved by IRE1α is ligated by RTCB to generate functional XBP1s mRNA. Unlike PERK and IRE1α, ATF6α released from BiP translocates to the Golgi apparatus through COPII vesicles, where the cytoplasmic region is cleaved by site-1 protease (S1P) and S2P. CREBH (cAMP response element-binding protein H), OASIS (old astrocyte specifically induced substance), Tisp40 (transcript induced in spermiogenesis), CREB3, and BBF2H7 (BBF2 human homolog on chromosome 7) are also activated through this mechanism.