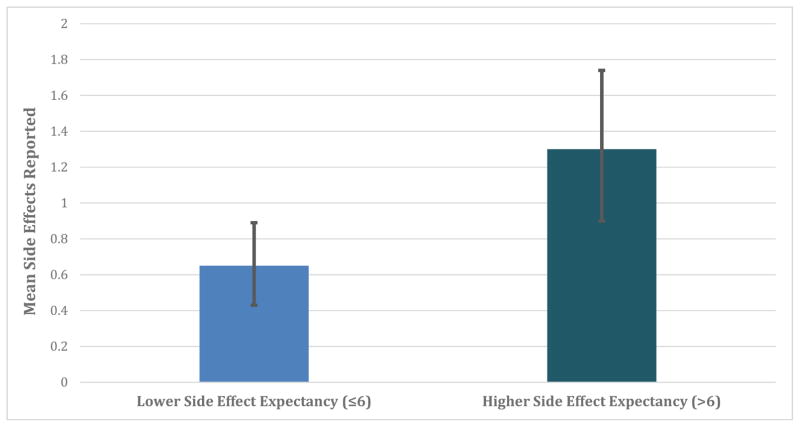
Figure 3. Illustration of the predicted number of potentially treatment-related side effects reported among patients with relatively higher versus lower side effect expectancy.
In a negative binomial regression, patients with higher baseline side effect expectancy reported more side effects potentially attributable to treatment (continuous analysis p = 0.038). 95% BcA bootstrapped confidence intervals displayed.