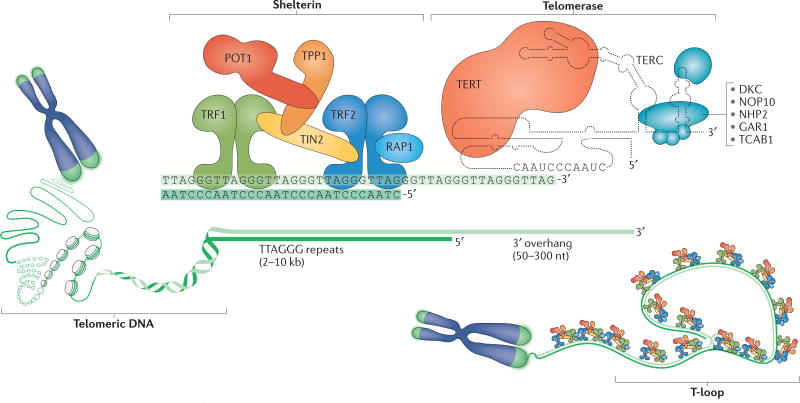
Figure 1. Composition and structure of the human telomere system.
Human telomeres comprise three components: telomeric DNA, the shelterin complex and the telomerase complex. Telomeric DNA consists of a long array of double-stranded TTAGGG repeats that culminates in a 50–300 nucleotide (nt) single-stranded 3′ overhang. This 3′ overhang invades double-stranded telomeric repeats to form a t-loop structure that is crucial for telomere function. Telomeric DNA protects chromosome ends through its association with the six-subunit shelterin complex. The length of telomeric repeats can be maintained by telomerase, which is composed of telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT), telomerase RNA template component (TERC) and several accessory proteins (blue). TERT synthesizes telomeric DNA de novo using TERC as a template, whereas the accessory factors contribute to the biogenesis and nuclear trafficking of telomerase. DKC, dyskerin; NHP2, non-histone protein 2; NOP10, nucleolar protein 10; POT1, protection of telomeres 1; RAP1, repressor/activator protein 1; TCAB1, telomerase Cajal body protein 1; TIN2, TRF1-interacting nuclear factor 2; TRF, telomeric repeat-binding factor.