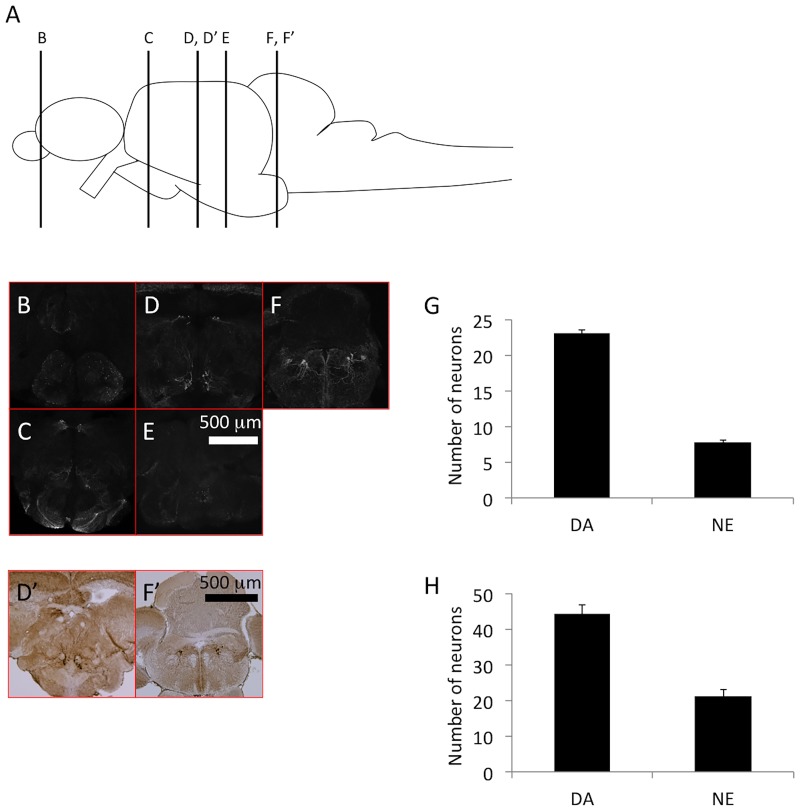
Fig 2. Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)+ neurons in the axial sections of zebrafish brains.
(A) The illustration indicates the position of sectioning in panels B–E. (B–E) Immunostaining of TH using a microsliced section of 6-month-old zebrafish. Different rostro–caudal levels show the localization of TH+ dopaminergic neurons in the olfactory bulb and subpallium (B); pretectum, posterior periventricular preoptic nucleus, and suprachiasmatic nucleus (C); pretectum, posterior tuberculum, and paraventricular organ (D); and posterior recess of the diencephalic ventricle (E). TH+ noradrenergic neurons are distributed in the locus coeruleus (F). (G) The number of TH+ neurons in the posterior tuberculum (dopaminergic neurons) and the locus coeruleus (noradrenergic neurons). The bars represent SEM (n = 10). (D’, F’) TH immunoreactivity in a paraffin section of a 6-month-old zebrafish. (H) The counted number of TH+ neurons using paraffin sections in the posterior tuberculum (dopaminergic neurons) and the locus coeruleus (noradrenergic neurons). Bars represent the SEM (n = 6).