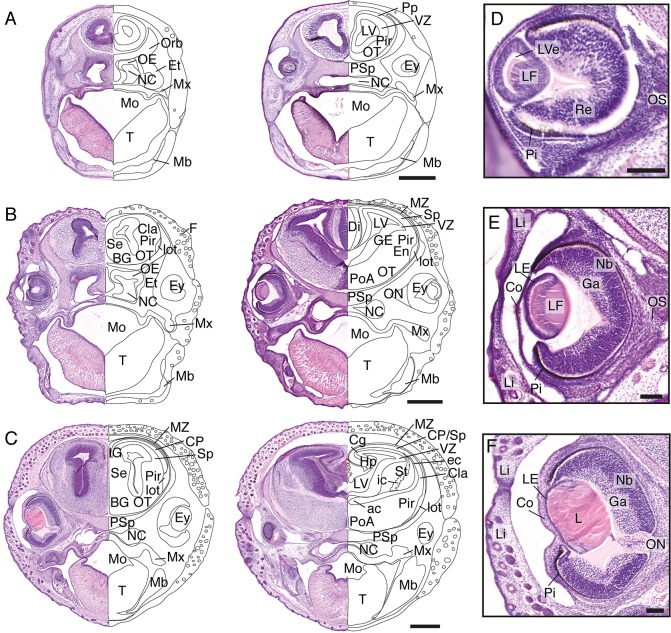
Fig 5. Craniofacial features of stages 19–21 S. crassicaudata.
Haematoxylin/eosin staining through rostral (left) and caudal (right) regions of the head of S. crassicaudata at stages 19 (A), 20 (B), and 21 (C) in the coronal plane (postnatal days 4–7, 8–11, and 12–15, respectively). Insets of the developing eye at corresponding ages (D-F, respectively). ac, anterior commissure; BG, basal ganglia; Cg, cingulate cortex; Cla, claustrum; Co, cornea; CP, cortical plate; ec, external capsule; En, endopiriform nucleus; Ey, eye; Et, ethmoid bone; F, follicle; Ga, ganglion layer; GE, ganglionic eminence; Hp, hippocampus; ic, internal capsule; IG, indusium griseum; L, lens; LE, lens epithelium; LF, lens fibres; Li, eyelid; lot, lateral olfactory tract; LV, lateral ventricle; LVe, lens vesicle; Mb, mandibulary process; Mo, mouth; Mx, maxillary process; MZ, marginal zone; NC, nasal cavity; Nb, neuroblastic layer; OE, olfactory neuroepithelium; ON, optic nerve; Orb, orbital bone; OS, optic stalk; OT, olfactory tubercle; Pi, pigment epithelium; Pir, piriform cortex; PoA, preoptic area; Pp, preplate; PSp; presphenoid bone; Re, retinal layer; Se, septum; Sp, subplate; St, striatum; SVZ, subventricular zone; T, tongue; VZ, ventricular zone. Scale bars: 500 μm (A-C), 100 μm (E-F).