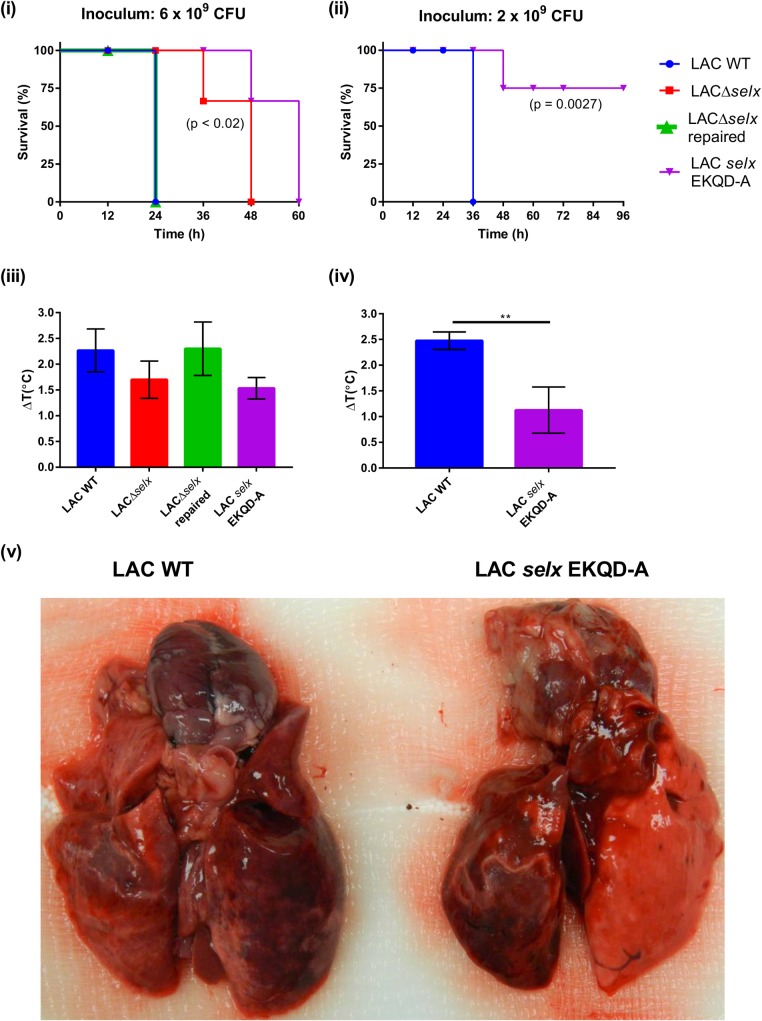
Fig 8. SElX contributes to lethality in a rabbit model of necrotising pneumonia by inhibiting neutrophil function.
Kaplan-Meier curves of % survival of rabbits infected with wild-type S. aureus LAC, LACΔselx, LACΔselx rep and LAC selx EKQD-A at a dose of 6x109 CFU (i) and S. aureus LAC and LAC selx EKQD-A at a dose of 2x109 CFU (ii), p-values stated are the results of log-rank (Mantel-Cox) tests. (iii) Increase in rabbit core temperature (ΔT°C) 12 h after pulmonary infection with LAC, LACΔselx, LACΔselx rep and LAC selx EKQD-A at a dose of 6x109 CFU (data plotted are the mean of three animals ± SD). (iv) Increase in rabbit core temperature (ΔT°C) 12 h after pulmonary infection with LAC and LAC selx EKQD-A at a dose of 2x109 CFU (data plotted are the mean of four animals ± SD, ** indicates statistical significance by unpaired, two-tailed students t-test p<0.003) (v) Gross pathology of lungs from rabbits infected with S. aureus strain LAC and LAC selx EKQD-A showing representative examples of haemorrhagic lesions.